The U.S. Millennium Cohort Study is a population-based prospective study that includes over 200,000 current and prior U.S. military service members.1,2
The cohort includes 4 panels of participants, the first of which was enrolled in 2001; subsequent panels were enrolled in 2004, 2007, and 2011. Questionnaires were sent to participants every 3 years to collect information on service-related experiences as well as mental, physical, and behavioral health. As such, the Millennium Cohort Study is uniquely positioned to leverage both administrative and self-reported data to help understand the effects of military service on the health of its members.
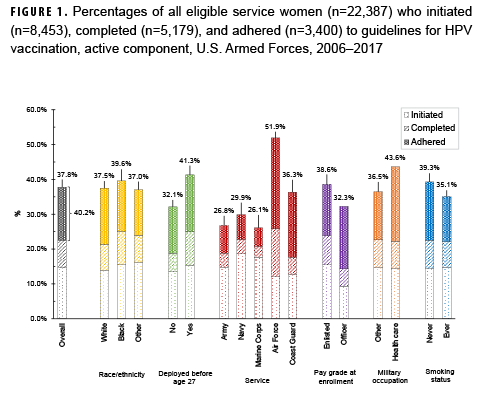
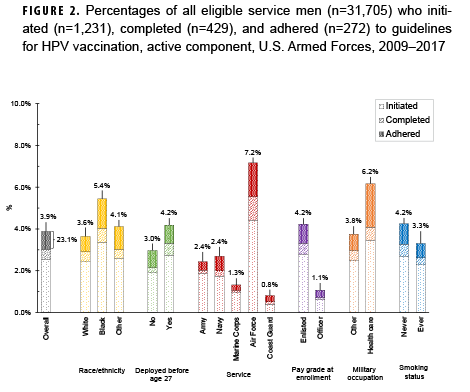
The analysis was restricted to active component members under age 26 in 2006 (women) or 2009 (men). The primary outcomes were human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine initiation, completion (3 doses), and adherence (3 doses within 1 year). Medical encounter and central immunization databases were used to identify those who had received the HPV vaccine through June 2017. The analysis sample included 22,387 female and 31,705 male Millennium Cohort Study participants.
Overall, among service women in the analysis sample, 37.8% initiated the HPV vaccine and 40.2% of initiators were adherent (Figure 1). Among service men in the analysis sample, 3.9% initiated the vaccine and 23.1% of initiators were adherent (Figure 2). Compared to their respective counterparts, members of the Air Force and those in health care occupations had higher percentages of initiation and adherence. Initiation and adherence percentages were lower among self-reported ever smokers (cigarette) compared to never smokers. No differences were observed for other selected measures such as depression, panic or anxiety, or problem drinking (data not shown).
Author affiliations: Deployment Health Research Department in the Military Population Health Directorate, Naval Health Research Center, San Diego, CA (Dr. Matsuno, Dr. Porter, Mr. Warner, CDR Wells); Leidos, Inc., San Diego, CA (Dr. Matsuno, Dr. Porter, Mr. Warner)
Disclaimer: The authors are military service members or employees of the U.S. Government, or contract employees of the Government. This work was prepared as part of their official duties. Title 17, U.S.C. §105 provides that copyright protection under this title is not available for any work of the U.S. Government. Title 17, U.S.C. §101 defines a U.S. Government work as work prepared by a military service member or employee of the U.S. Government as part of that person’s official duties.
This work was supported by the Military Operational Medicine Research Program under work unit no. 60002. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, or the U.S. Government.
The study protocol was approved by the Naval Health Research Center Institutional Review Board in compliance with all applicable Federal regulations governing the protection of human subjects. Research data were derived from an approved Naval Health Research Center, Institutional Review Board protocol number NHRC.2000.0007.
References
- Gray GC, Chesbrough KB, Ryan MA, et al. The Millennium Cohort Study: a 21-year prospective cohort study of 140,000 military personnel. Mil Med. 2002;167(6):483–488.
- Ryan MA, Smith TC, Smith B, et al. Millennium Cohort: enrollment begins a 21-year contribution to understanding the impact of military service. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(2):181–191.