-
MHS Home
-
News & Gallery
-
Articles
-
Surveillance Snapshot: Incidence of Rickettsial Diseases Among Active and Reserve Component Service Members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2010–2018
Surveillance Snapshot: Incidence of Rickettsial Diseases Among Active and Reserve Component Service Members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2010–2018
 Dorsal view of a female American dog tick, Dermacentor variabilis. Credit: CDC/Gary O. Maupin
Dorsal view of a female American dog tick, Dermacentor variabilis. Credit: CDC/Gary O. Maupin
Rickettsial diseases are vector-borne, bacterial infections that cause acute febrile illness throughout the world. Because symptoms of rickettsial diseases are often non-specific in nature and overlap with other febrile diseases with similar epidemiology, their diagnosis is challenging. The diagnostic difficulties likely contribute to the historical underreporting of cases of these diseases.
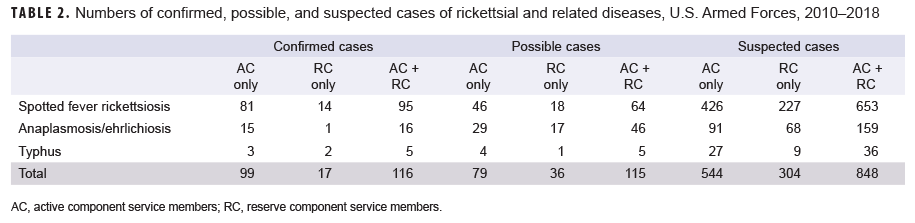
In 2018, the MSMR published a report on the surveillance of vector-borne disease in active and reserve component service members that included estimates of incident cases of rickettsial and related diseases during the surveillance period from 2010 through 2016.1 The analysis for this snapshot used similar methodology but restricted the analysis to rickettsial diseases and extended the surveillance period through 2018. A "confirmed" case was defined as an individual identified through a reportable medical event (RME) report of a rickettsial or related disease that was described as "confirmed" by having met specific laboratory and/or epidemiologic criteria.2 A "possible" case was defined by a record of hospitalization with a diagnosis for a rickettsial disease (Table 1) in any diagnostic position. A "suspected" case was defined by either an RME of a rickettsial disease without laboratory or epidemiologic confirmation or a record of an outpatient medical encounter with a diagnosis of a rickettsial disease in the first or second diagnostic position. An individual could be counted once per lifetime for each type of rickettsial disease. Individuals diagnosed as a case before the start of the surveillance period were excluded. Confirmed cases were prioritized over possible and suspected cases, respectively (Table 2).
These data indicate that a continued multidisciplinary focus on preventive measures to counter the threat of these diseases is warranted. Most important are effective vector control and adherence to personal protective measures.
References
- O'Donnell FL, Stahlman S, Fan M. Surveillance for vector-borne diseases among active and reserve component service members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2010–2016. MSMR. 2018;25(2):8–15.
- Defense Health Agency. Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch. Armed Forces Reportable Medical Events. Guidelines and Case Definitions, 2017. https://health.mil/reference-Center/Publications/2017/07/17/Armed-Forces-Reportable-Medical-Events-Guidelines. Accessed 17 July 2019.

You also may be interested in...
Report
Mar 1, 2024
 .PDF |
1.34 MB
.PDF |
1.34 MB
The March 2024 MSMR features a comparison of 2018 estimates from the HRBS and the PHA on tobacco and nicotine use among the U.S. military active component; followed by a report on coverage of HIV PrEP among active duty service members in 2023; supplemented by a Surveillance Snapshot of HIV PrEP prescriptions in 2023 in the active component; then a ...
Report
Feb 1, 2024
 .PDF |
1.07 MB
.PDF |
1.07 MB
This is the February 2024 issue of MSMR—Medical Surveillance Monthly Report.
Report
Jan 1, 2024
 .PDF |
1.11 MB
.PDF |
1.11 MB
January 2024 issue of MSMR
Report
Dec 1, 2023
 .PDF |
3.39 MB
.PDF |
3.39 MB
MSMR volume 30 number 12, December 2023
Report
Nov 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1.07 MB
.PDF |
1.07 MB
MSMR November 2023 volume 30 issue 11
Report
Oct 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1.29 MB
.PDF |
1.29 MB
The October 2023 Medical Surveillance Monthly Report (MSMR) provides a review of the incidence of colorectal cancer among active component service members from 2010 to 2022; followed by a study of force protection risks in AFRICOM, INDOPACOM, and SOUTHCOM due to rapid diagnostic test failures for P. falciparum malaria from 2016 to 2022; then an update ...
Report
Sep 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1.30 MB
.PDF |
1.30 MB
The September 2023 MSMR provides the annual update of routine screening for antibodies to HIV among the active and reserve components of the U.S. Armed Forces; followed by a serological survey of Ross River virus (RRV) infection among U.S. Marine expeditionary forces who train in Australia; followed by a Surveillance Snapshot of the 10 leading ...
Report
Aug 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1.02 MB
.PDF |
1.02 MB
The August 2023 MSMR provides the most recent data from the active surveillance program for acute respiratory disease and Group A Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcus among U.S. Army basic trainees; then summarizes the case report of an extensively resistant E. coli in a returning traveler at Hawai'i's Tripler Army Medical Center; followed by a Surveillance ...
Report
Jul 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1.30 MB
.PDF |
1.30 MB
This continuation of the June issue, which published the annual quantification of health care provided by the Military Health System, continues with the impacts of various illnesses and injuries in 2022 among deployed service members; medical evacuations out of theaters of military operation; health care provision to non-service member MHS ...
Report
Jun 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1.55 MB
.PDF |
1.55 MB
This annual issue quantifies the impacts of various illnesses and injuries in 2022 among members of the active component of the U.S. Armed Forces as well as the U.S. Coast Guard; health care burden metrics include the total number of medical encounters, including hospitalizations and ambulatory services, as well as numbers and types of individuals ...
Report
May 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1023.59 KB
.PDF |
1023.59 KB
The May 2023 MSMR reintroduces a monthly reportable medical event (RME) summary for the active component and MHS beneficiaries; then features a review of enhanced mpox outbreak case detection among MHS beneficiaries through ESSENCE (Electronic Surveillance System for the Early Notification of Community-based Epidemics); followed by a report on ...
Report
Apr 1, 2023
 .PDF |
978.69 KB
.PDF |
978.69 KB
April 2023 of MSMR, the Medical Surveillance Monthly Report
Report
Mar 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1021.43 KB
.PDF |
1021.43 KB
March 2023 issue of MSMR, the Medical Surveillance Monthly Report
Report
Feb 1, 2023
 .PDF |
965.54 KB
.PDF |
965.54 KB
This issue of the peer-reviewed monthly journal published by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division (AFHSD) features the articles: Changing of the Guard: MSMR’s Second Editor-in-Chief Retires; Brief Report: Hospitalizations Among Active Duty Members of the U.S. Coast Guard, Fiscal Year 2021; Historical Perspective: The Critical Role of Disease ...
Report
Jan 1, 2023
 .PDF |
1.22 MB
.PDF |
1.22 MB
A monthly publication of the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division. This issue of the peer-reviewed journal contains the following articles: Incidence and management of chronic insomnia, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2012 to 2021; Changes in the prevalence of overweight and obesity and in the incidence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes ...
You are leaving Health.mil
The appearance of hyperlinks does not constitute endorsement by the Department of Defense of non-U.S. Government sites or the information, products, or services contained therein. Although the Defense Health Agency may or may not use these sites as additional distribution channels for Department of Defense information, it does not exercise editorial control over all of the information that you may find at these locations. Such links are provided consistent with the stated purpose of this website.
You are leaving Health.mil
View the external links disclaimer.
Last Updated: July 11, 2023