Surveillance Snapshot: Influenza Immunization Among U.S. Armed Forces Healthcare Workers, Aug. 2014–April 2019
 181129-N-GR847-3000
ARABIAN GULF (Nov. 29, 2018) Hospitalman Jay Meadows, from Weaver, Ala., administers an influenza vaccine to a Sailor during a regularly scheduled deployment of the Essex Amphibious Ready Group (ARG) and 13th Marine Expeditionary Unit (MEU). The Essex ARG/13th MEU is flexible and persistent Navy-Marine Corps team deployed to the U.S. 5th Fleet area of operations in support of naval operations to ensure maritime stability and security in the Central Region, connecting to the Mediterranean and the Pacific through the western Indian Ocean and three strategic choke points. (U.S. Navy photo by Mass Communication Specialist 3rd Class Reymundo A. Villegas III)
181129-N-GR847-3000
ARABIAN GULF (Nov. 29, 2018) Hospitalman Jay Meadows, from Weaver, Ala., administers an influenza vaccine to a Sailor during a regularly scheduled deployment of the Essex Amphibious Ready Group (ARG) and 13th Marine Expeditionary Unit (MEU). The Essex ARG/13th MEU is flexible and persistent Navy-Marine Corps team deployed to the U.S. 5th Fleet area of operations in support of naval operations to ensure maritime stability and security in the Central Region, connecting to the Mediterranean and the Pacific through the western Indian Ocean and three strategic choke points. (U.S. Navy photo by Mass Communication Specialist 3rd Class Reymundo A. Villegas III)
The U.S. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that all health care personnel be vaccinated against influenza to protect themselves and their patients.1 The Joint Commission's standard on infection control emphasizes that individuals who are infected with influenza virus are contagious to others before any signs or symptoms appear. The Joint Commission requires that health care organizations have influenza vaccination programs for practitioners and staff and that they work toward the goal of 90% receipt of influenza vaccine. Within the Department of Defense, seasonal influenza immunization is mandatory for all uniformed personnel and for health care personnel who provide direct patient care and is recommended for all others (excluding those who are medically exempt).2–4
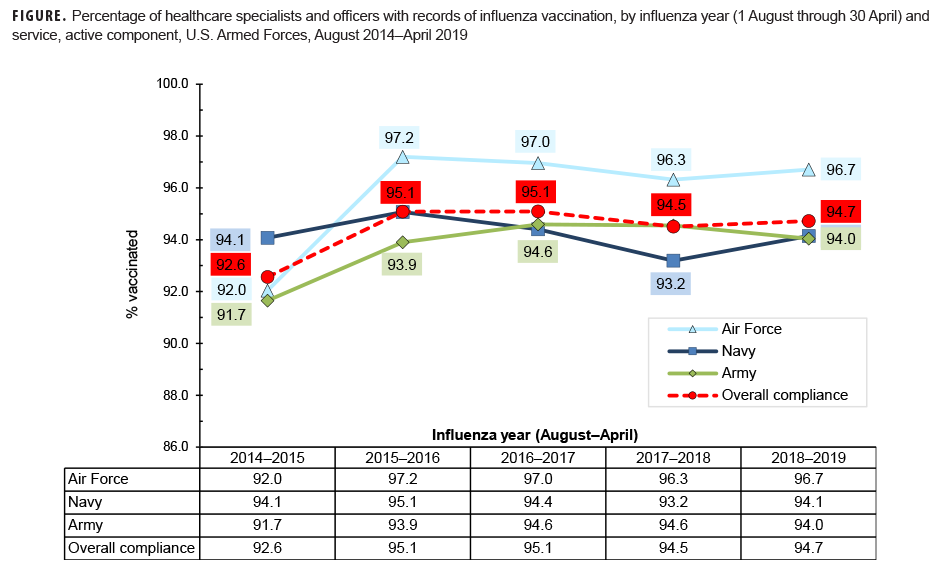
This snapshot covers a 5-year surveillance period (Aug. 2014–April 2019) and presents the documented percentage compliance with the influenza immunization requirement among active component health care personnel of the Army, Navy, and Air Force. During the 2018–2019 influenza season, each of the 3 services had compliance rates of 94.0% or higher among health care personnel (Figure). For all services together, the compliance rate was 94.7%, very similar to the rate from the previous year.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Immunization of health-care personnel: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2011;60(RR-7):1–45.
- Headquarters, Departments of the Army, the Navy, the Air Force, and the Coast Guard. Army Regulation 40-562, BUMEDINST 6230.15B, AFI 48-110_IP, CG COMDTINST M6230.4G. Medical Services: Immunizations and Chemoprophylaxis for the Prevention of Infectious Diseases. 7 Oct. 2013.
- Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs. Policy for Mandatory Seasonal Influenza Immunization for Civilian Health Care Personnel Who Provide Direct Patient Care in Department of Defense Military Treatment Facilities. Health Affairs Policy 08-005. 4 April 2008.
- Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs. Addition of Pandemic Influenza Vaccine or Novel Influenza Vaccine to the Policy for Mandatory Seasonal Influenza Immunization for Civilian Health Care Personnel Who Provide Direct Patient Care in Department of Defense Military Treatment Facilities. Health Affairs Policy 11-010. 28 July 2011.
You also may be interested in...
Article
Feb 1, 2024
This report summarizes 2003 to 2021 survey administration and content of the U.S. Marine Recruit Assessment Program, a cross-sectional, baseline survey of U.S. Marine recruits that is administered at Marine Corps Recruit Depot, San Diego.
Report
Feb 1, 2024
 .PDF |
1.07 MB
.PDF |
1.07 MB
This is the February 2024 issue of MSMR—Medical Surveillance Monthly Report.
Article
Jan 1, 2024
This report describes ivermectin prescription fill rates among U.S. active component service members over time during the early phases of the COVID-19 pandemic. Ivermectin prescription fill rates increased among active component service members early in the COVID-19 pandemic when misinformation about the effectiveness of ivermectin for prevention and ...
Article
Jan 1, 2024
This descriptive epidemiologic study describes weight loss prescription medication prevalence among active component service members from January 2018 through June 2023.
Article
Jan 1, 2024
This editorial provides a bibliometric summary and thematic analysis for articles published in MSMR over a 5-year period, from January 2019 through December 2023.
Article
Jan 1, 2024
This report provides linear trends of selected vector-borne diseases, over a 13-year surveillance period, among Armed Forces service and non-service member beneficiaries diagnosed at installations within the Northern Command (NORTHCOM), Africa Command (AFRICOM), Central Command (CENTCOM), European Command (EUCOM), Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM), or ...
Article
Jan 1, 2024
Each month the MSMR publishes an update of reportable medical events documented in the Disease Reporting System internet by health care providers and public health officials throughout the Military Health System, for monitoring, controlling, and preventing the occurrence and spread of diseases of public health interest or readiness importance.
Article
Jan 1, 2024
Dr. Robert Johnson, the fourth editor-in-chief of the MSMR, introduces himself to readers and communicates his editorial goals for the journal.
Report
Jan 1, 2024
 .PDF |
1.11 MB
.PDF |
1.11 MB
January 2024 issue of MSMR
Article
Dec 1, 2023
Chlamydia, by far the most frequently reported medical event (RME) with the MHS, declined by 17% in October, to 1,190 cases, from 1,437 cases (adjusted) in September; this follows a 15% decline from August to September. Gonorrhea, the second highest RME, declined 15% in October, to 192 cases reported cases in September, from 225 cases (adjusted). ...
Article
Dec 1, 2023
The proportions of women and Hispanic service members increased from 2018 to 2022, while the proportions of non-Hispanic White active component service members and those under 20 years of age decreased.
Article
Dec 1, 2023
This data analysis identified a small number of reported chikungunya cases, and even fewer hospitalizations, suggesting that risk of chikungunya virus disease to U.S. service member readiness is small.
Article
Dec 1, 2023
Compared to civilians, active component service members may have increased risk of SLE due to greater exposure to environmental risk factors such as silica dust and ultraviolet radiation, and higher rates of post-traumatic stress disorder, which have been linked to SLE.
Article
Dec 1, 2023
The Medical Surveillance Monthly Report (MSMR) shares the news of the recent death of our colleague, Valerie Williams.
Article
Dec 1, 2023
Command decisions for balancing risks have differed in every pandemic of the past century because those decisions occurred in a broader cultural context of acceptable health risks tied to available technology and scientific knowledge.
You are leaving Health.mil
The appearance of hyperlinks does not constitute endorsement by the Department of Defense of non-U.S. Government sites or the information, products, or services contained therein. Although the Defense Health Agency may or may not use these sites as additional distribution channels for Department of Defense information, it does not exercise editorial control over all of the information that you may find at these locations. Such links are provided consistent with the stated purpose of this website.
You are leaving Health.mil
View the external links disclaimer.
Last Updated: July 11, 2023