The U.S. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that all health care personnel be vaccinated against influenza to protect themselves and their patients.1 The Joint Commission's standard on infection control emphasizes that individuals who are infected with influenza virus are contagious to others before any signs or symptoms appear. The Joint Commission requires that health care organizations have influenza vaccination programs for practitioners and staff and that they work toward the goal of 90% receipt of influenza vaccine. Within the Department of Defense, seasonal influenza immunization is mandatory for all uniformed personnel and for health care personnel who provide direct patient care and is recommended for all others (excluding those who are medically exempt).2–4
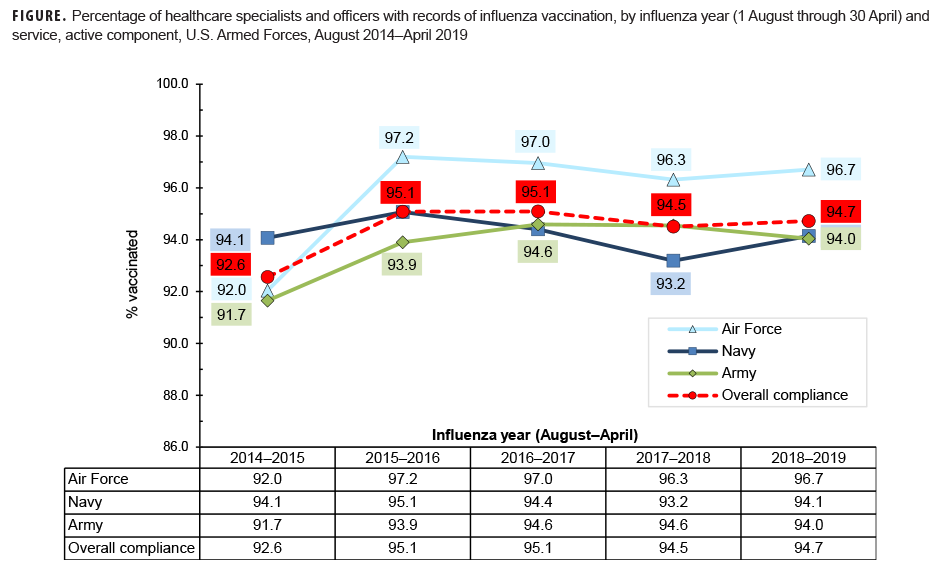
This snapshot covers a 5-year surveillance period (Aug. 2014–April 2019) and presents the documented percentage compliance with the influenza immunization requirement among active component health care personnel of the Army, Navy, and Air Force. During the 2018–2019 influenza season, each of the 3 services had compliance rates of 94.0% or higher among health care personnel (Figure). For all services together, the compliance rate was 94.7%, very similar to the rate from the previous year.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Immunization of health-care personnel: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2011;60(RR-7):1–45.
- Headquarters, Departments of the Army, the Navy, the Air Force, and the Coast Guard. Army Regulation 40-562, BUMEDINST 6230.15B, AFI 48-110_IP, CG COMDTINST M6230.4G. Medical Services: Immunizations and Chemoprophylaxis for the Prevention of Infectious Diseases. 7 Oct. 2013.
- Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs. Policy for Mandatory Seasonal Influenza Immunization for Civilian Health Care Personnel Who Provide Direct Patient Care in Department of Defense Military Treatment Facilities. Health Affairs Policy 08-005. 4 April 2008.
- Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs. Addition of Pandemic Influenza Vaccine or Novel Influenza Vaccine to the Policy for Mandatory Seasonal Influenza Immunization for Civilian Health Care Personnel Who Provide Direct Patient Care in Department of Defense Military Treatment Facilities. Health Affairs Policy 11-010. 28 July 2011.