The Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division, as part of its surveillance mission, periodically conducts studies of cancer incidence among U.S. military service members. However, service members are likely lost to follow-up from the Department of Defense cancer registry and Military Health System data sets after leaving service and during periods of time not on active duty.
Therefore, an ongoing cancer surveillance study sought linkage with civilian state cancer registries through the Virtual Pooled Registry Cancer Linkage System (VPR-CLS) supported by the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries (NAACCR) and funded by the National Cancer Institute. These civilian state registries require the inclusion of all malignant or in situ neoplasms classified by the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, Third Edition (ICD-O-3), with the exception of carcinoma in situ of the Click to closeCervixThe cervix is the lower, narrow end of the Click to closeuterusAlso known as the womb, the uterus is the female reproductive organ where a baby grows. uterus (womb). The cervix connects the uterus to the vagina (birth canal).cervix and squamous/basal cell carcinomas of the skin.
Since 2004, non-malignant benign/borderline primary tumors of the brain and central nervous system (CNS) have also been included as reportable cancers.1 The VPR-CLS performs a Phase I and Phase II linkage process to identify members of the study population who have been diagnosed with a reportable cancer. In Phase I, an aggregate total of matched cancer cases are provided by each state cancer registry after performing the linkage behind their respective firewalls. In Phase II, after approval of additional applications and data use agreements, line-level data on each of the cancer cases can be provided. This report describes the Phase I linkage results.
Methods
A roster of over 10.9 million current and former service members was provided to the VPR-CLS to facilitate the Phase I linkage after Defense Health Agency (DHA) Institutional Review Board (IRB) study approval as a public health surveillance activity. The roster included current and former members of the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps who had a duty military occupation specialty code contained in the Defense Medical Surveillance System. This included active, reserve, and guard component members serving at any period through 2017, beginning in 1985 for Army members and 1990 for members of all other services. Individuals who joined service after 2017 were not included. Cancer case counts were quantified as high-quality matches defined by a probabilistic linkage algorithm to identify matched pairs above a certain threshold when matched according to various combinations of SSN, name, sex, and date of birth. The case counts provided by the Phase I match results include all reportable cancers, as defined by the respective civilian state registry standards.1 Furthermore, individuals with multiple primary cancers are counted for each primary cancer and for each state of residence at diagnosis, according to tumor inclusion and reportability standards.1
Results
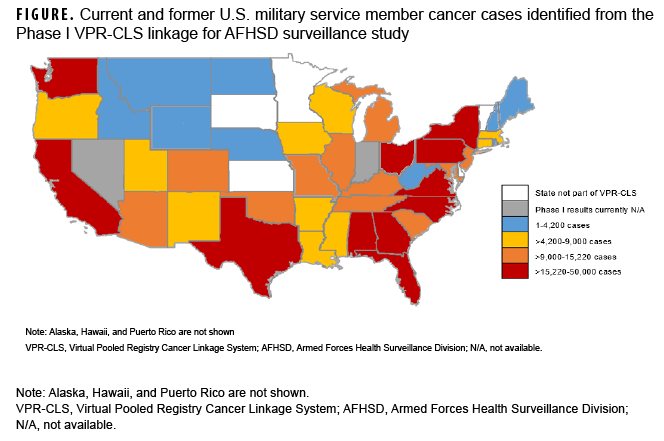
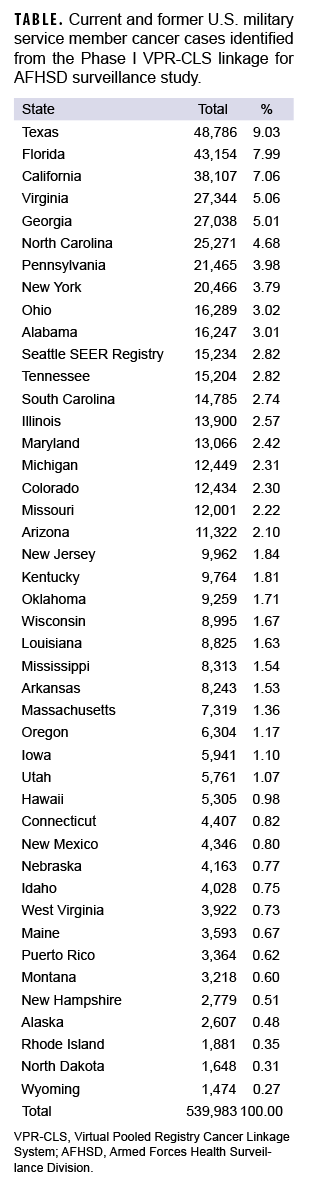
At the time of this report, Phase I match results were available for 44 out of 46 states in the VPR-CLS. Cases were identified as early as 1973 for some state cancer registries, and up through the most recently available data (2020 for most states). A total of 539,983 cases were identified among current and former military service members (Table). Not surprisingly, the highest numbers of cases were identified in the some of the most highly populated states, including Texas, Florida, and California (Table, Figure).
Editorial Comment
Most previous military cancer surveillance studies have relied on data from the DoD cancer registry, the VA central cancer registry, TRICARE medical billing data, or a combination of these sources.2–5 Similar to the DoD cancer registry, the VPR-CLS contains information about tumor staging, patient demographics, treatment, and vital status. The primary advantages of VPRCLS for military cancer surveillance are its potential for enabling more complete surveillance among personnel who are diagnosed and treated in civilian facilities and that it is more likely to include former service members no longer on active duty. In addition, all state registries are certified annually by NAACCR for compliance with quality standards of completeness, timeliness, and accuracy.6 Phase I counts allow investigators to determine the number of cancers identified in each state prior to completing the more intensive application and review processes for Phase II.
Limitations to the VPR-CLS include a lag in data availability, as cancer registries generally make their data available 24 months after the close of a diagnosis year in order to provide the most complete and consolidated data. In addition, although the VPR-CLS provides a systematic process for linkage with multiple civilian state cancer registries, 8 states in the VPR-CLS currently require separate applications and 20 require separate data use agreements for Phase II. Finally, it should be noted that the numbers presented in this report may not include cancers diagnosed in individuals who are receiving care exclusively at military treatment facilities. At the time of this report, only 4 states had completed the requirements and agreements for DoD cancer registry data sharing. Given the large number of high-quality matches identified via the Phase I linkage process, this system serves as a promising tool for future military cancer studies. More information about the VPR-CLS can be found at: https://www.naaccr.org/about-vpr-cls/.
Author affiliations
Defense Health Agency, Public Health Directorate, Silver Spring, MD (Dr. Stahlman, CAPT Wells); North American Association of Central Cancer Registries, Springfield, IL (Ms. Clerkin, Ms. Kohler); Information Management Services, Inc., Rockville, MD (Mr. Howe); National Institute of Health/National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD (Dr. Cronin).
References
- North American Association of Central Cancer Registries (NAACCR). Chapter III: Standards for Tumor Inclusion and Reportability. Accessed June 17, 2022. Accessed 24 June 2022. http://datadictionary.naaccr.org/default.aspx?c=3&Version=22
- Zhu K, Devesa SS, Wu H, et al. Cancer incidence in the U.S. military population: comparison with rates from the SEER program. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18(6):1740–1745.
- Robbins AS, Pathak SR, Webber BJ, et al. Malignancy in U.S. Air Force fighter pilots and other officers, 1986-2017: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0239437.
- Webber BJ, Tacke CD, Wolff GG, et al. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Among Fighter Aviators in the United States Air Force. J Occup Environ Med. 2022;64(1):71–78.
- Lee T, Williams VF, Clark LL. Incident diagnoses of cancers in the active component and cancer- related deaths in the active and reserve components, U.S. Armed Forces, 2005–2014. MSMR. 2016;23(7):23–31.
- North American Association of Central Cancer Registries (NAACCR). Certification Criteria. Accessed 24 June 2022. https://www.naaccr.org/certification-criteria/