This snapshot highlights unadjusted metrics of opioid prescription fills among active duty and retired service members using data from the Pharmacy Data Transaction Service of the Military Health System (MHS). The metrics described include
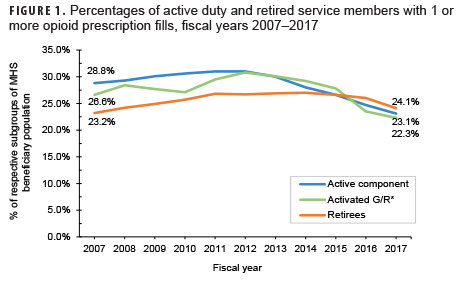
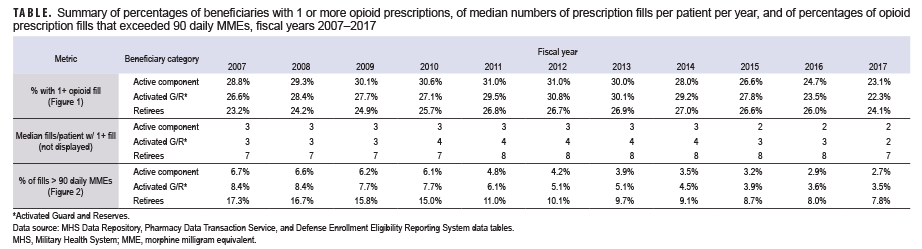
- the percentage of active component, reserve component, and military retirees who filled at least 1 opioid prescription (therapeutic class = opiate agonist) in a given year (Figure 1, Table);
- the median number of fills per year among those with at least 1 fill (Table); and
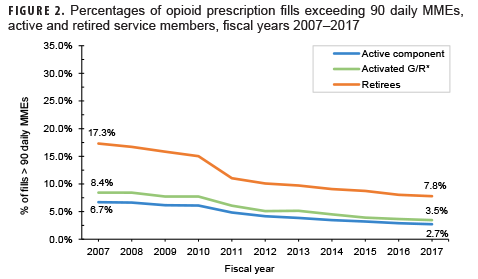
- the percentage of opioid fills that exceeded 90 daily morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) (Figure 2).a
Despite decreasing fill rates in recent years, nearly 1 in 4 active duty and retired service members had a filled opioid prescription in 2017 (Figure 1). Active duty and activated Guard/Reserve members who received an opioid prescription had a median of 2 fills per patient in 2017, while retirees had a median of 7 fills per patient (Table). Moreover, a higher percentage of retirees' opioid prescriptions were for high-dose prescriptions (as determined by MMEs)1,2 compared to active duty and activated Guard/Reserve, although rates were not adjusted for age (Figure 2). While increased duration and prescriptions greater than 90 MME per day are not necessarily problematic in and of themselves, both are risk factors for potential misuse and may be indicators of potentially concerning prescribing practices.3 These findings highlight the importance of tracking opioid fills in the MHS, monitoring patients with opioid prescriptions, expanding surveillance efforts to assess prescription practices, and limiting opportunities for opioid misuse and abuse. Despite substantial rates of opioid prescription fills, opioid use disorders are diagnosed infrequently among service members in the MHS (0.2% prevalence from 2010–2015).4 It is important to emphasize and sustain initiatives such as the Defense Health Agency's Opioid Prescriber Safety Training Program as well as regulatory guidance5 aimed at facilitating the responsible use of this important facet of pain management.
aDaily MME = (strength per unit) x (number of units/days' supply) x (MME conversion factor).1,2,5
Author affiliations: Psychological Health Center of Excellence, J-9 Research and Development Directorate of the Defense Health Agency (Mr. Peters, Dr. Kincaid, Ms. Quah, Ms. Greenberg, Dr. Curry); Salient CRGT, Inc. (Mr. Peters, Dr. Kincaid, Ms. Quah, Ms. Greenberg)
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Opioid oral morphine milligram equivalent (MME) conversion factors. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Prescription-Drug-Coverage/PrescriptionDrugCovContra/Downloads/Opioid-Morphine-EQ-Conversion-Factors-Aug-2017.pdf. Accessed 24 June 2019.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Calculating total daily dose of opioids for safer dosage. https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/calculating_total_daily_dose-a.pdf. Accessed 24 June 2019.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vital signs: opioid prescribing. https://www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/pdf/2017-07-vitalsigns.pdf. Published July 2017. Accessed 24 June 2019.
- Office of the Secretary of Defense. Report to Congress on prescription drug abuse. https://health.mil/Reference-Center/Reports/2016/04/15/Prescription-Drug-Abuse. Published March 2016. Accessed 24 June 2019
- Defense Health Agency. Procedural Instruction 6025.04. Pain Management and Opioid Safety in the MHS. 8 June 2018.