Abstract
The term gallbladder disease refers to a variety of conditions of the gallbladder and the biliary tract. The more common of these conditions are cholelithiasis (gallstones) and cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), and these conditions often are treated with cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal). During the 2014–2018 surveillance period, 8,008 active component service members were identified as incident cases of gallbladder disease. The crude overall incidence rate of gallbladder disease was 1.2 per 1,000 person-years; the crude annual rate decreased very slightly during the period. A total of 6,470 active component service members underwent incident cholecystectomies. Almost all (97.4%) were performed laparoscopically, and the majority were performed in outpatient settings (65.2%). The number of hospital bed days per open cholecystectomy far exceeded those per laparoscopic cholecystectomy. However, the number of hospital bed days per open cholecystectomy markedly decreased throughout the period. Gallbladder disease and cholecystectomies were more common among service members who were female, American Indian/Alaska Native or Hispanic, older, in the Air Force, and in health care occupations. Clinicians should continue to advocate for lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and a diet low in fat and cholesterol, that could prevent gallbladder disease. Similarly, continued Department of Defense-wide initiatives to promote healthy lifestyles could also help prevent gallbladder disease and maintain the health of the force.
What Are the New Findings?
Annual rates of gallbladder disease in active component service members during the 2014–2018 period declined slightly compared to the 2004–2013 period, when rates increased. About 1,601 new cases of gallbladder disease and 1,294 cholecystectomies occurred annually during the surveillance period. Over 97% of cholecystectomies were performed via laparoscopy, a technique that reduces the duration of recovery compared to an open surgical approach.
What Is the Impact On Readiness and Force Health Protection?
Gallbladder disease and cholecystectomy are not rare, affecting approximately 1 out of every 1,000 service members per year. Their availability for duty and deployability are adversely impacted during the evaluation, surgical treatment, and convalescence associated with gallbladder disease. Risk factors for such disease that are susceptible to modification include excess body weight, a diet with a high fat or cholesterol content, diabetes, and certain medications.
Background
The gallbladder is a small (3-inch long), hollow, pear-shaped organ located in the upper right section of the abdomen, just under the right lobe of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver and releases it into the small intestine after a meal to help dissolve fat. Gallbladder disease, including cholelithiasis (gallstones), is common in the U.S. and often results in cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). Cholecystitis can result in severe pain in the upper right or center abdomen, pain that spreads in the right shoulder or back, tenderness over the abdomen when touched, nausea, vomiting, or fever, particularly after a large or fatty meal. Although these symptoms may be avoided by reducing the amount of fatty and highly processed foods as well as whole milk dairy products consumed, gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy) is recommended when symptoms become frequent, recurrent, or more severe. Gallbladder removal is typically achieved with the minimally invasive laparoscopic technique, which involves inserting a camera and dissection tools through several small incisions in the abdominal wall.1 Open cholecystectomy, which requires a 4- to 6-inch incision1 and longer hospitalization and convalescence periods, is only used if the laparoscopic method is not possible or cannot be completed safely because the gallbladder is severely inflamed, infected, or scarred from other operations.
Gallbladder disease is related to nonmodifiable risk factors, such as being female, being older than 40 years of age, having a family history of gallbladder disease, and being of American Indian or Hispanic descent,2–8 as well as modifiable risk factors, such as being overweight or obese, rapid fluctuations in body weight, a high-fat or high-cholesterol diet, diabetes, and certain medications.2–8 Pregnancy and parity have also been shown to be associated with an increased risk of gallstone formation.2,7,8
It is estimated that over 20 million people in the U.S. have gallstones, and symptoms caused by gallstones are a primary gastrointestinal cause for hospital admissions and health care utilization.3,7,9 Furthermore, over 500,000 laparoscopic cholecystectomies are performed annually in the U.S., making it one of the most common abdominal surgeries performed, costing roughly $6.5 billion per year.7,10
A previous MSMR report showed very slight increases in the crude annual incidence rates of gallbladder disease and cholecystectomies among active component members of the U.S. Armed Forces from 2004 through 2013.11 Although outcomes related to laparoscopic cholecystectomy are generally good, an increase in the rates of gallbladder disease could negatively impact the readiness of the force. This report updates the counts and rates of newly diagnosed gallbladder disease and cholecystectomies among U.S. active component service members during 2014–2018.
Methods
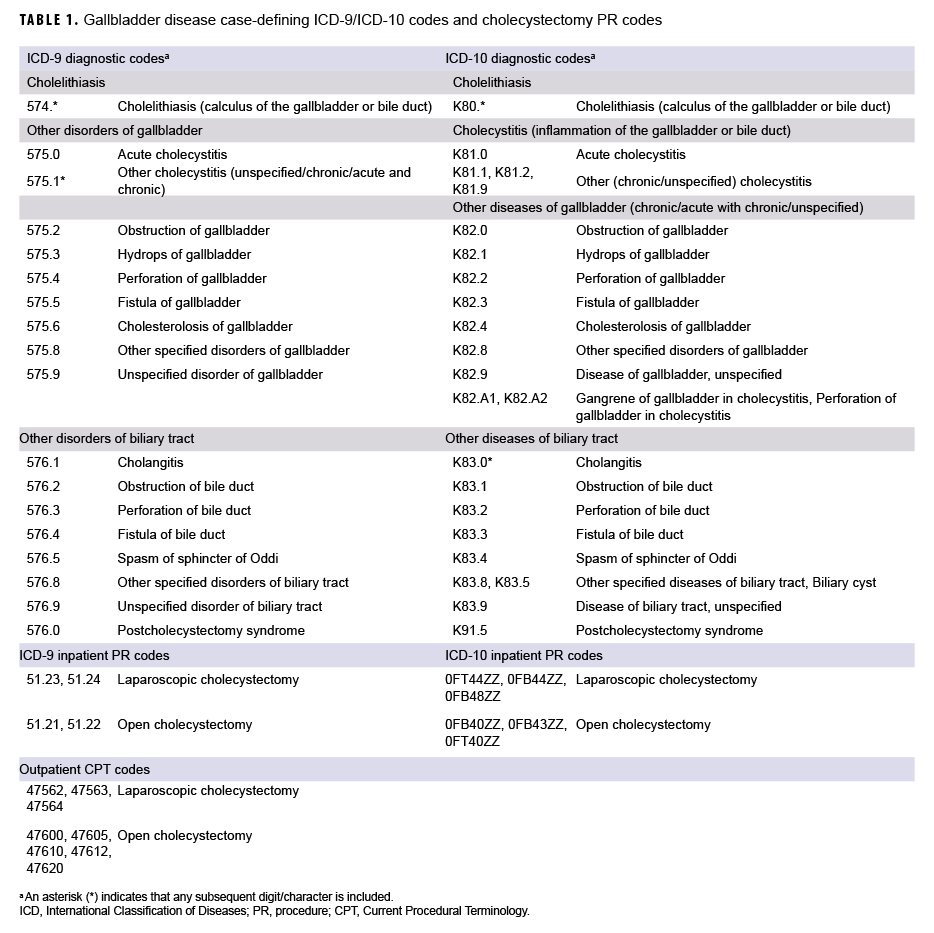
The surveillance period was 01 Jan. 2014 through 31 Dec. 2018. The surveillance population included all active component service members of the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps who served at any time during the surveillance period. For the purposes of this report, "gallbladder disease" included not only cholelithiasis and cholecystitis, but also other or unspecified disorders of the gallbladder and other or unspecified disorders of the biliary tract (Table 1). An incident (first-ever) case of gallbladder disease was defined as an inpatient encounter with a case-defining International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code in the primary diagnostic position or 2 outpatient encounters with a relevant ICD code in the primary diagnostic position (Table 1). An individual was considered a case once per lifetime. The type of gallbladder disease was categorized based on the diagnosis specified in the primary diagnostic position for the incident encounter. A prevalent case was defined in the same manner as an incident case, but it occurred before the start of the surveillance period. Individuals with 1 encounter before the start of the surveillance period and 1 after were classified as prevalent cases. Person-time was censored at the incident event and prevalent cases were removed from the study population. Those with diagnoses in non-primary positions were also excluded.
A case of cholecystectomy was defined as an inpatient encounter with a procedure code (PR code) for cholecystectomy in any position or an outpatient encounter with a Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code for cholecystectomy in any position (Table 1). An individual was considered a case of cholecystectomy only once per lifetime; cholecystectomies were analyzed separately from gallbladder disease cases. For each incident case of cholecystectomy, if an individual had records of multiple procedures performed, inpatient encounters were preferentially selected over outpatient encounters and open cholecystectomies were prioritized over laparoscopic cholecystectomies.
Among the incident gallbladder disease cases that were identified during the surveillance period, the number and percentage of cases with a cholecystectomy encounter whose date was on or after their incident gallbladder disease diagnosis were identified. The average time between incident gallbladder disease diagnosis and first subsequent cholecystectomy encounter was calculated. Similarly, for all individuals with an incident cholecystectomy identified during the surveillance period, the number and percentage of cases with gallbladder disease diagnoses (made in any diagnostic position) during an encounter on or before the date of their incident cholecystectomy were identified. The average time between incident cholecystectomy and first gallbladder disease diagnosis was calculated.
Finally, a burden analysis was performed to identify the morbidity and health care burden of gallbladder disease and cholecystectomy during the surveillance period. For this analysis, all inpatient and outpatient encounters with a diagnosis of gallbladder disease in the primary diagnostic position during the study period were included. No more than 1 encounter per person per day was counted. If there were multiple encounters on the same day, inpatient encounters were prioritized over outpatient encounters. The total number of encounters, hospital bed days, and individuals affected were calculated according to standard MSMR burden methodology.12
Results
Gallbladder disease
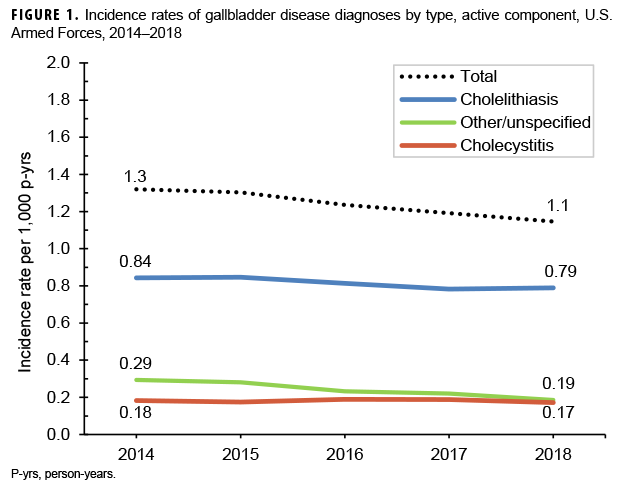
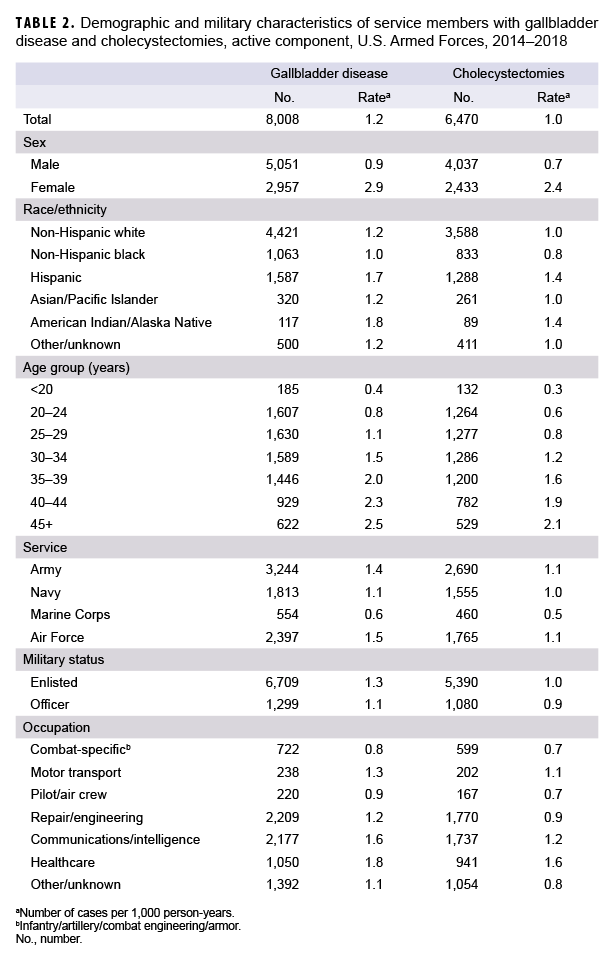
During the 5-year surveillance period, 8,008 incident diagnoses of gallbladder disease were documented on inpatient or outpatient medical records of active component service members (Table 2). The crude overall rate of incident gallbladder disease diagnoses was 1.2 per 1,000 person-years (p-yrs). A majority of the cases were diagnosed as cholelithiasis (65.8%); cholecystitis was reported among 14.6% of cases, and other/unspecified disorders of the gallbladder/biliary tract were reported among 19.6% (data not shown). Crude annual incidence rates of all gallbladder disease diagnoses (total) decreased very slightly during the surveillance period from 1.3 per 1,000 p-yrs in 2014 to 1.1 per 1,000 p-yrs in 2018 (Figure 1).
Compared to their respective counterparts, service members who were female, American Indian/Alaska Native or Hispanic, in the Air Force or Army, and in health care occupations had higher overall incidence rates of gallbladder disease (Table 2). Overall incidence rates increased approximately linearly with increasing age (Table 2).
Cholecystectomy
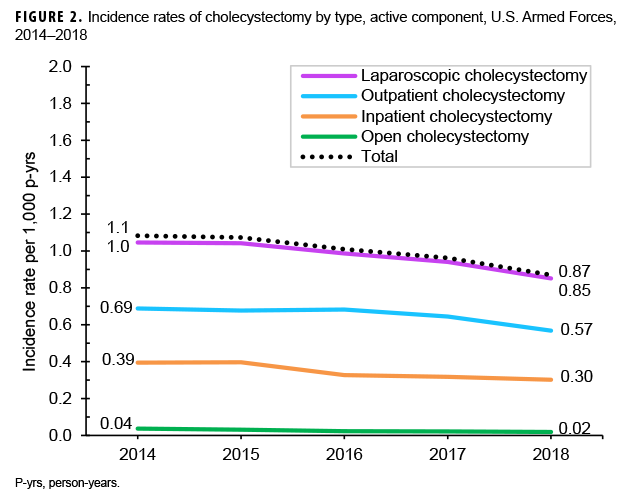
From 2014 through 2018, a total of 6,470 active component service members underwent cholecystectomies (Table 2). The overall incidence rate of cholecystectomy was 1.0 per 1,000 p-yrs. Slightly more than three-fifths of all the procedures were performed in the outpatient setting (n=4,220; 65.2%), and the vast majority were performed laparoscopically (n=6,300; 97.4%) (data not shown). There was a small decrease in the annual rate of total cholecystectomy procedures during the surveillance period from 1.1 per 1,000 p-yrs in 2014 to 0.87 per 1,000 p-yrs in 2018, with slight decreases observed in the rates of inpatient and outpatient cholecystectomies as well as open and laparoscopic cholecystectomies (Figure 2).
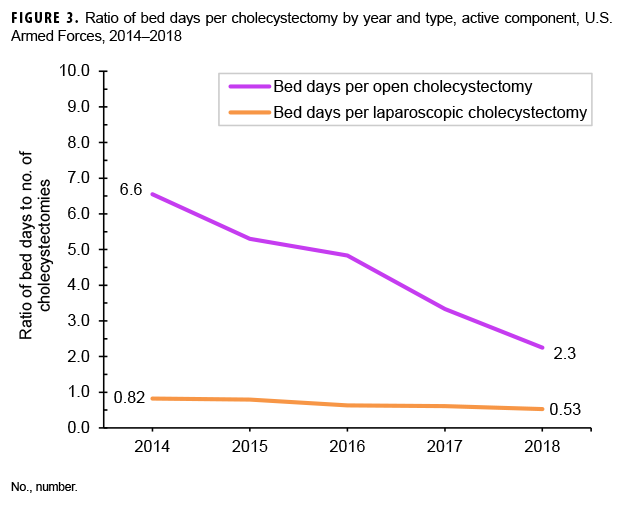
On average, there were 0.7 hospital bed days per laparoscopic cholecystectomy and 4.8 bed days per open cholecystectomy (data not shown). The number of hospital bed days per laparoscopic cholecystectomy remained under 1 bed day during each year of the surveillance period and was stable throughout the surveillance period (Figure 3). Bed days per open cholecystectomy decreased each year from a high of 6.6 bed days in 2014 to a low of 2.3 bed days in 2018.
Relationship between gallbladder disease diagnoses and cholecystectomy
Of the 8,008 individuals who were identified as incident cases of gallbladder disease, 5,720 (71.4%) were also identified as having a cholecystectomy performed following their first-ever case-defining encounter. Among the gallbladder disease cases who had cholecystectomies, 23.3% had their first-ever gallbladder encounter on record on the same day as the cholecystectomy. The average interval between first-ever gallbladder disease diagnosis and surgery was 44 days (data not shown).
Among the 6,470 service members who were identified as having undergone cholecystectomy, 98.7% (n=6,388) had at least 1 gallbladder disease-related encounter before their cholecystectomy (data not shown). Among the cholecystectomy cases, the average number of days between their first-ever gallbladder disease encounter and cholecystectomy was slightly more than 4 months (123 days).
Editorial Comment
The annual rates of gallbladder disease declined very slightly between 2014 and 2018. Gallbladder disease was newly diagnosed in approximately 1,600 active component service members on average each year between 2014 and 2018. A total of 6,470 incident cholecystectomies were performed during this period.
A previously published MSMR report documented a slight overall increase in the annual rates;11 however, data toward the end of the surveillance period may have indicated the beginning of the slight decline documented in this report. It is possible that the increase shown in that 2014 report tracked with the increase in obesity rates,11 as obesity is a known risk factor for gallbladder disease. Indeed, the Millennium Cohort study, MSMR analyses, and the recently published Department of Defense (DOD) Health of the Force have shown that the prevalence of obesity among service members, while still lower than the prevalence among the general U.S. population, has been increasing.13–15 However, the current analysis cannot clarify the reasons for the decreases seen. It should be noted, though, that the increases and decreases documented in both reports represent very slight changes that may not be clinically or epidemiologically meaningful.
Consistent with studies of the prevalence of gallbladder disease in the U.S. and elsewhere, the overall rates of gallbladder disease were highest among females, American Indians/Alaska Natives or Hispanics, and those in the oldest age groups. As indicated in the previous MSMR report, the higher overall rates among those in the Air Force and health care occupations may be because those groups have comparatively higher proportions of females and older individuals.11
In line with the slightly declining trend observed in the crude annual rates of gallbladder disease, the rates of both inpatient and outpatient and open and laparoscopic cholecystectomies also decreased slightly. Laparoscopic cholecystectomies performed in the outpatient setting continue to be the standard of care.1 The number of hospital bed days per laparoscopic cholecystectomy stayed under 1 bed day throughout the surveillance period. The number of bed days per open cholecystectomy in particular has shown a steep and steady decline throughout the 5-year surveillance period.
The mean number of days between the incident gallbladder disease encounter and cholecystectomy among service members with gallbladder disease was 44 days (range = 0 days–4.8 years), which suggests that clinicians and affected individuals are not waiting long before gallbladder removal. This may be related to a variety of factors, including surgical options with a very short recovery period, access to free health care, and the military's need to maintain a fit and ready force. On the other hand, the mean number of days between incident gallbladder disease encounter and cholecystectomy among all those who had a cholecystectomy (123 days; range = 0 days–18.7 years) increased slightly from the previous MSMR report (82 days; range = 0 days–14.8 years).
The number of cholecystectomy cases exceeded the number of incident gallbladder disease cases who underwent cholecystectomy because some individuals did not have gallbladder disease case-qualifying encounters (e.g., the individual had only 1 outpatient encounter or had a case-defining diagnosis reported in a non-primary diagnostic position) and were not counted in this report. Furthermore, other gallbladder encounters may have occurred before entrance into military service, before the surveillance period, or in health care settings outside the Military Health System (MHS).
Interpretation of the findings in this report should be done with consideration of some limitations. This report likely underestimates the rates of cholecystectomy after a gallbladder disease diagnosis, as some service members may have left military service or were lost to follow-up before surgery. Moreover, the surveillance period may have ended before some of the cases that were identified later in the period underwent surgery. Another limitation of the current analysis is related to the implementation of MHS GENESIS, the new electronic health record for the MHS. For 2017–2018, medical data from sites that were using MHS GENESIS are not available in the Defense Medical Surveillance System. These sites include Naval Hospital Oak Harbor, Naval Hospital Bremerton, Air Force Medical Services Fairchild, and Madigan Army Medical Center. Therefore, medical encounter and person-time data for individuals seeking care at any of these facilities during 2017–2018 were not included in the analysis.
Although the rates of gallbladder disease and cholecystectomies declined slightly among all active component service members during the study period, gallbladder disease and cholecystectomies are not rare and the rates are higher among those with identified risk factors for gallstone formation. Clinicians should continue to advocate for lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and a diet low in fat and cholesterol, that could prevent gallbladder disease. Similarly, continued DOD-wide initiatives to promote healthy lifestyles could also help prevent gallbladder disease and maintain the health of the force.
References
- Johns Hopkins University. Cholecystectomy. http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/test_procedures/gastroenterology/cholecystectomy_92,P07689/. Accessed 19 June 2019.
- Mayo Clinic. Diseases and conditions: gallstones. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/basics/definition/con-20020461. Accessed 19 June 2019.
- Stinton LM, Shaffer EA. Epidemiology of gallbladder disease: cholelithiasis and cancer. Gut Liver. 2012;6(2):172–187.
- Nakeeb A, Comuzzie AG, Martin L, et al. Gallstones: genetics versus environment. Ann Surg. 2002;235(6):842–849.
- Arevalo JA, Wollitzer AO, Corporon MB, Larios M, Huante D, Ortiz MT. Ethnic variability in cholelithiasis—an autopsy study. West J Med. 1987;147;44–47.
- Miquel JF, Covarrubias C, Villaroel L, et al. Genetic epidemiology of cholesterol cholelithiasis among Chilean Hispanics, Amerindians, and Maoris. Gastroenterol. 1998;115(4):937–946.
- Figueiredo JC, Haiman C, Porcel J, et al. Sex and ethnic/racial-specific risk factors for gallbladder disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017;17(1):153.
- Grodstein F, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ. A prospective study of symptomatic gallstones in women; relation with oral contraceptives and other risk factors. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;84(2):207–214.
- Afdhal NH, Zakko SF. Gallstones: epidemiology, risk factors and prevention. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/gallstones-epidemiology-risk-factors-and-prevention?search=cholelithiasis&topicRef=654&source=see_link. Accessed 19 June 2019.
- Kapoor T, Wrenn SM, Callas PW, Abu-Jaish W. Cost analysis and supply utilization of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Minim Invasive Surg. 2018;Dec:7838103.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch. Gallbladder disease and cholecystectomies, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2004–2013. MSMR. 2014;21(6):8–11.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch. Absolute and relative morbidity burdens attributable to various illnesses and injuries, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2018. MSMR. 2019;26(5):2–10.
- Clark LL, Stephen TB. Update: Diagnosis of overweight and obesity, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2011–2015. MSMR. 2016;23(9):9–13.
- Rush T, LeardMann CA, Crum-Cianflone NF. Obesity and associated adverse health outcomes among US military members and veterans: findings from the Millennium Cohort Study. Obesity. 2016;24(7):1582–1589.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch. DOD Health of the Force 2018. Falls Church, VA: Defense Health Agency; 2019.