The Millennium Cohort Study is a prospective study that was initiated in 2001 and includes over 200,000 current and prior U.S. military service members.1 Questionnaires are sent to participants approximately every 3 years to collect information on service related experiences as well as mental, physical, and behavioral health. Compliance with contemporary cervical cancer screening recommendations was determined among service women enrolled in the Millennium Cohort Study during 2003–2015. Current cervical cancer screening recommendations call for a Pap smear alone every 3 years in women aged 21–65 years or for a human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA test with or without a Pap test every 5 years for women aged 30–65 years.2 Women were considered eligible for screening in a given year if they were aged 21–62 years on the last day of the year, had served in the active component (i.e., at least 9 months in active component pay and strength rosters) for the concurrent year and 2 years before, had not had a Click to closehysterectomyA partial or total surgical removal of the Click to closeuterusAlso known as the womb, the uterus is the female reproductive organ where a baby grows. uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and other surrounding structures. hysterectomy, and had not separated from the military. Women were considered compliant with screening recommendations between 2003–2015 if they had a medical report of a Pap smear in the year of assessment or prior 2 calendar years. Women were also considered compliant with screening recommendations in 2013–2015 if they had HPV DNA testing completed within the previous 5 years.
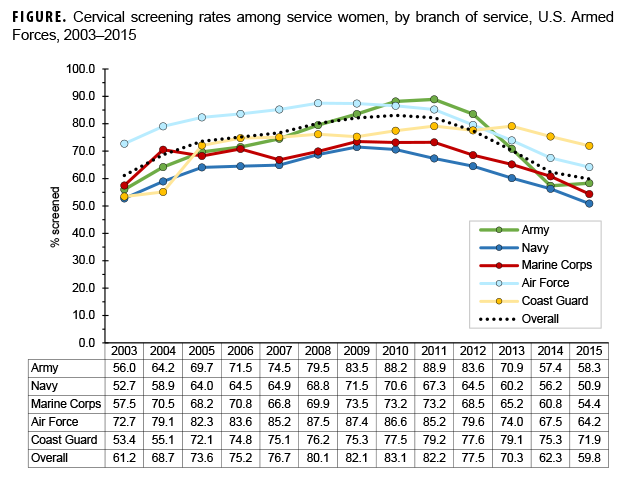
Overall, among U.S. service women in the Millennium Cohort Study, the compliance rate increased from 61.2% in 2003 to a peak of 83.1% in 2010 then declined to a low of 59.8% in 2015 (Figure). During the first 7 years of the study period, compliance was highest among Air Force personnel. Between 2013 and 2015, compliance was highest among Coast Guard personnel. Compliance was lowest among Navy personnel in all but 1 year (2004) of the 13-year period. Compliance was also consistently higher for service women who had initiated the HPV vaccine than for women who had not (on average 6.3% higher). No differences in compliance were observed by cigarette smoking status, which was used as a surrogate measure of other health behaviors.
Author affiliations: Deployment Health Research Department in the Military Population Health Directorate, Naval Health Research Center, San Diego, CA (Dr. Matsuno, Dr. Porter, Mr. Warner, CAPT Wells); Leidos, San Diego, CA (Dr. Matsuno, Dr. Porter, Mr. Warner).
Disclaimer: One of the authors of this work is a military service member or employee of the U.S. Government. This work was prepared as part of their official duties. Title 17, U.S.C. §105 provides that copyright protection under this title is not available for any work of the U.S. Government. Title 17, U.S.C. §101 defines a U.S. Government work as work prepared by a military service member or employee of the U.S. Government as part of that person’s official duties. This report was supported by the Military Operational Medicine Research Program under work unit no. 60002. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, or the U.S. Government.
References
Bulleted List for References
- Gray GC, Chesbrough KB, Ryan MA, et al. The Millennium Cohort Study: a 21-year prospective cohort study of 140,000 military personnel. Mil Med. 2002;167(6):483–488.
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Final recommendation statement. Cervical cancer: screening. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/cervical-cancer-screening?ds=1&s=pap. Accessed 9 April 2020.