Caregiver Guide Supports Service Members and Veterans with TBI
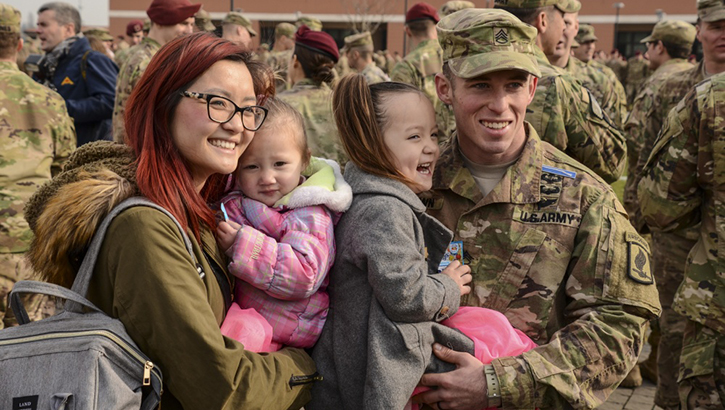 Caregivers play a vital role for TBI patient recovery (Photo by: Army Lt. Col. John Hall, 173rd Airborne Brigade)
Caregivers play a vital role for TBI patient recovery (Photo by: Army Lt. Col. John Hall, 173rd Airborne Brigade)
After her husband sustained a traumatic brain injury from a rocket attack in Iraq in 2006, Tiffany Bodge searched for information to help cope with her new role as a caregiver.
Retired Air Force Lt. Col. Ryan Bodge struggled with short-term memory loss, sometimes taking his evening medication in the morning. The pain from his TBI-induced chronic migraines made it hard to concentrate.
However, when Tiffany Bodge discovered the Traumatic Brain Injury Center of Excellence's Caregiver Guide in 2021, she found tools to help the couple manage his recovery. Now, when he goes for treatment, they work on lists of questions to ask the doctor. If he forgets a conversation, he asks for the details to be repeated.
"I look at caregiving as collaborative, we have to do it together," Tiffany Bodge said. "I'm here to make his life easier, to help him in a way that gives him the freedom to continue to live his life that isn't really defined by parameters. The TBI is going to limit him in the things that he's capable of doing, but you know, we can figure out a way that he can still enjoy life and do the things that he wants to do. He just has to do them in a different way."
Research shows family support leads to better recovery, and addressing caregiver needs has long been a focus of TBICoE. In a recent report to Congress, TBICoE states, "Family education and support are critical components of acute inpatient rehabilitation; however, needs are common in chronic stages of TBI, highlighting the importance of ongoing services through chronic stages of TBI."
To provide those services to family and friends like the Bodges, TBICoE released an updated Traumatic Brain Injury: A Guide for Caregivers of Service Members and Veterans earlier this month.
"[The guide] gives you a really good understanding of the different types of TBI and the severity, what you're going to be dealing with in the short term, [and] what may possibly be in the long term," explained Tiffany Bodge, who was asked to review and provide feedback on the new guide. "But I also like the fact that it talks about the recovery process, and that the caregiver is an integral part of recovery."
The guide includes the following:
- Resources to address mild TBI, also known as a concussion, which accounts for over 80% of TBIs in the military reported by TBICoE. The earlier version addressed only moderate, severe, and penetrating TBI.
- New content on post-traumatic stress disorder, substance misuse, and intimacy (from both the patient and caregiver perspective), and information on suicide and caregiver burnout.
- Interactive features allowing users to easily navigate the guide and find relevant information that meets their needs.
 Some service members with TBI can experience vision problems. Navy Cmdr. Matthew Lawrence, a physician deployed in support of Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve, checks Army Sgt. Jeremy Woodrow’s responsiveness during a mass casualty training exercise at Erbil Air Base in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, Jan. 16, 2020. (Photo by: Army Spc. Angel Ruszkiewicz)
Some service members with TBI can experience vision problems. Navy Cmdr. Matthew Lawrence, a physician deployed in support of Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve, checks Army Sgt. Jeremy Woodrow’s responsiveness during a mass casualty training exercise at Erbil Air Base in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, Jan. 16, 2020. (Photo by: Army Spc. Angel Ruszkiewicz)
"The best thing about the caregiver guide is that it is written for caregivers. It has practical tips. You might be experiencing this, [so] try this. These practical tips from people that you know have already gone through it really, really helps," said Melissa Comeau, whose husband Stephen, a staff sergeant in the U.S. Marine Corps, sustained the first of his multiple TBIs around 2004, and who has PTSD, as well.
Comeau also reviewed the guide and liked the content provided on the relationship between TBI and PTSD. "It helped me reach out to the correct type of providers and ask for the correct type of treatment and also ask the right kind of questions to get my husband on a path to the best recovery he could have," she said.
In addition to being interactive and available on desktop and mobile devices, the guide is shorter - only 154 pages.
Both the original and current guides relied on expertise from across the Department of Defense. Congressionally mandated by the National Defense Authorization Act of 2007, the first guide involved collaboration among TBI experts, survivors, and experienced caregivers of service members and veterans with TBIs. Similarly, the new version drew on input from TBICoE, the National Intrepid Center of Excellence, the Psychological Health Center of Excellence, and the Department of Veterans Affairs.
Comeau remains hopeful about how she and her husband will continue to manage his TBI.
"Resources like the Caregiver Guide are an important tool for providers to offer to the caregivers of their patients who are recovering from a TBI," said Navy Capt. Scott Pyne, a physician and the TBICoE division chief. "Each caregiver can use the guide to meet their own unique needs, which can be wide ranging. This is the beauty of the guide. Whether it's using the resource section to lookup local caregiver groups or someone that they can physically connect with, or using the glossary to remind them of the jargon that was used during a medical appointment. The guide can empower the caregiver in their role supporting someone close to them who has been diagnosed with a TBI. It also can help improve the providers' relationship with their patients by arming them and their caregivers with the information needed to support their recovery."
The Traumatic Brain Injury Center of Excellence is a congressionally mandated collaboration of the Departments of Defense and Veterans Affairs to promote state-of-the-science care from point-of-injury to reintegration for service members, veterans, and their families to prevent and mitigate the consequences of mild to severe traumatic brain injury. The center is a division of the Defense Health Agency Research and Development Directorate.
For more information on the Traumatic Brain Injury: A Guide for Caregivers of Service Members and Veterans and other TBICoE programs, visit: health.mil/TBICoE.