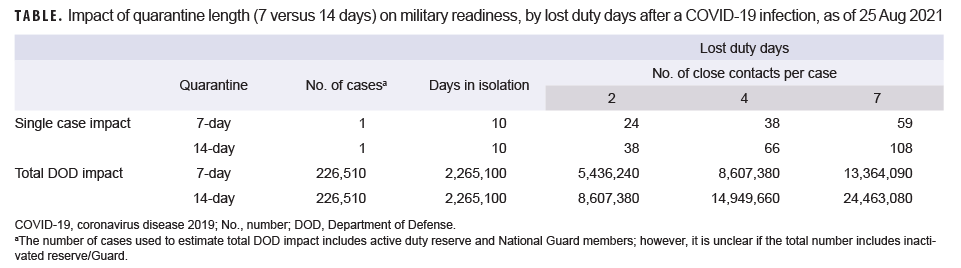
Since the start of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the Department of Defense (DOD) has reported 226,510 cases of COVID-19 among military members as of 25 Aug. 2021.1 Managing COVID-19 infections and implementing quarantines of their contacts could alter the training and mission plans for most, if not all, military units. Although there was robust prognostication regarding the impact of COVID-19 on lost duty days in the early months of the pandemic,2,3 little has been published in this area since then.
Simple modeling can provide an important estimate of the impact of COVID-19 on lost duty days among U.S. service members. The model used in this analysis assumes that each reported case undergoes 10 days of isolation and allows for variation in the number of close contacts (e.g., low [2], medium [4] and high [7]) and the length of quarantine (7 or 14 days). This model estimates the impact of a single COVID-19 case for each of the possible values of close contacts and quarantine length and also extrapolates the DOD-wide impact in terms of number of lost duty days (Table).
The model is a gross approximation of lost duty days and may both underestimate and overestimate lost duty days due to several factors. The model ignores the lost duty days of the 34 deaths and 2,036 hospitalizations among military service members reported by DOD since the start of the pandemic.1 This model also does not take into account the indirect lost duty days affecting service members charged with special duties in tracking, caring for, and administratively handling service members in isolation and quarantine. It also ignores the lost duty days of cases diagnosed in family members and the impact of lost duty days on non-military close contacts, including family members and DOD civilian employees. Furthermore, this model does not estimate the cumulative impact on unit readiness of multiple simultaneous or consecutive COVID-19 infections within a command. Finally, this model may overestimate lost duty days by including weekend days and it is unclear if the military members included in the DOD case report1 include inactivated reserve/Guard members who may not be on duty.
The COVID-19 pandemic has adversely impacted the availability of service members to unit Commanders. Using this model, one can estimate a best-case scenario of the loss of 0.71% of all duty days, with a worst-case scenario of the loss of around 3.2% of all duty days in the DOD during the period of March 1, 2020 to Aug. 25, 2021. When this loss is placed in the context of 3 to 8 members of a unit being unavailable for a mission, deployment, or training event due to a single infection, the impact on unit readiness is easily seen. Preventing a single case has a far-reaching impact on readiness, conserving 24–98 duty days of availability to Commanders. Although some service members were able to recover a portion of these lost days by teleworking, they represent the minority and were primarily among higher ranks.
Prevention of COVID-19 infections can have a significant positive impact on service member availability for missions and training. Ongoing efforts using all available infection prevention tools, including immunization, non-pharmaceutical interventions, and policies designed to prevent new infections should be pursued by Commanders and leaders at all levels of the DOD in order to optimize training tempo and readiness activities.
Author affiliations: Department of Public Health, Madigan Army Medical Center, U.S. Army, WA (LTC Mease and CPT Smith).
Disclaimer: The views expressed are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy of the Department of the Army, the Department of Defense, or the U.S. Government.
References
- Coronavirus: DOD Response. U.S. Department of Defense. Published 3 May 2021. Accessed 25 Aug. 2021. https://www.defense.gov/Explore/Spotlight/Coronavirus
- Burke T, Dycus C, O'Hanlon M, Reid E, Worst J. COVID-19 and military readiness: Preparing for the long game. Brookings. Published April 22, 2020. Accessed 4 May 2021. https://www.brookings.edu/blog/order-from-chaos/2020/04/22/covid-19-and-military-readiness-preparing-for-the-long-game
- DiEuliis D, Junor L. Ready or Not: Regaining Military Readiness during COVID19. Inst Natl Strateg Stud. Published online April 10, 2020. Accessed 4 May 2021. https://inss.ndu.edu/Media/News/Article/2145282/ready-or-not-regaining-military-readiness-during-covid19