Myths & facts about the vax - debunking common COVID-19 vaccine myths
 The COVID-19 vaccine has been mandated across the Department of Defense and despite its demonstrated effectiveness and safety, a host of myths have left some Airmen and Guardians hesitant to receive it. While social media posts and some news outlets may make it harder to keep up with what is fact or fiction, the science is clear … approved COVID-19 vaccines work (Photo by: U.S. Air Force).
The COVID-19 vaccine has been mandated across the Department of Defense and despite its demonstrated effectiveness and safety, a host of myths have left some Airmen and Guardians hesitant to receive it. While social media posts and some news outlets may make it harder to keep up with what is fact or fiction, the science is clear … approved COVID-19 vaccines work (Photo by: U.S. Air Force).
9/29/2021
By:
Air Force Surgeon General Public Affairs Office
The COVID-19 vaccine has been mandated across the Department of Defense and despite its demonstrated effectiveness and safety, a host of myths have left some Airmen and Guardians hesitant to receive it. While social media posts and some news outlets may make it harder to keep up with what is fact or fiction, the science is clear...approved COVID-19 vaccines work.
Here is a breakdown of the most common myths surrounding COVID-19 vaccines, and the facts behind each myth:
Myth: COMIRNATY is not the same as the PFIZER-BIONTECH COVID-19 vaccine.
Truth: It is common for vaccine names to change after receiving full Food and Drug Administration approval for branding purposes. COMIRNATY and Pfizer-BioNTech are biologically and chemically the same vaccine. The FDA approved Pfizer-BioNTech for licensing and branding as COMIRNATY August 23 for people 16 years and older. Critically, the Emergency Use Authorization for Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine continues and covers the 12-15 year old population.
In accordance with FDA guidance, COMIRNATY has the same formulation and can be used interchangeably with the FDA-authorized Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Providers can use doses distributed under the EUA, to administer the vaccination series as if the doses were the licensed vaccine.
Myth: There were no people of color involved or represented in the research or development of the vaccine.
Truth: COVID-19 has taken a heavy and disproportionate toll on people of color, particularly Black adults. Historically, people of color have been underrepresented in clinical trials. Therefore, ensuring racial and ethnic diversity in clinical trials for development of COVID-19 vaccines has been particularly important. Diversity within clinical trials for a COVID-19 vaccine also ensures safety and effectiveness across populations. Findings show that Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine safety and efficacy were similar for people of color and white participants.
The FDA offered nonbinding recommendations that strongly encouraged the enrollment of populations most affected by COVID-19, specifically racial and ethnic minorities. Both Pfizer and Moderna worked to ensure that people of color were included in their trials, with Moderna even slowing down enrollment to enroll more racial and ethnic minorities. There have also been efforts on the community side. Historically Black colleges and universities participated in COVID-19 vaccine trials and encouraged participation among their communities. The purposeful encouragement to increase racial and ethnic groups in these trials have achieved greater diversity than many previous trials for other drugs.
Myth: The COVID-19 vaccine can cause problems with breast tissue and lead to breast cancer.
Truth: There is no evidence that COVID-19 vaccines cause problems with breast tissue or would lead to breast cancer. The mRNA vaccines are processed by your body near the injection site and activate immune system cells that then travel through the lymph system to nearby lymph nodes. In this manner, an individual may experience swelling under the arm where the vaccine was administered due to swelling of the lymph node. The vaccines are not affecting hormone levels, nor are they traveling throughout the body or affecting other body organs, such as breast tissue. Swollen lymph nodes can show up in a mammogram even if women can't feel them. Hence, the Society of Breast Imaging recommends women delay any routine mammography scheduled within four weeks after their most recent COVID-19 vaccination.
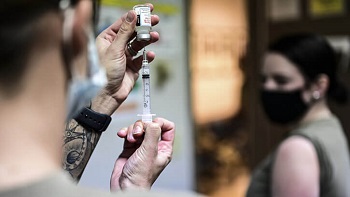 Air Force Master Sgt. Luca Farkas, 911th Aeromedical Staging Squadron aeromedical technician, fills a syringe with the COVID-19 vaccine at the Pittsburgh International Airport Air Reserve Station, Pennsylvania in Jan. 2021 (Photo by: Joshua Seybert, 911th Airlift Wing).
Air Force Master Sgt. Luca Farkas, 911th Aeromedical Staging Squadron aeromedical technician, fills a syringe with the COVID-19 vaccine at the Pittsburgh International Airport Air Reserve Station, Pennsylvania in Jan. 2021 (Photo by: Joshua Seybert, 911th Airlift Wing).
Myth: If I take COMIRNATY while breastfeeding, my baby will be infected with COVID-19.
Truth: COVID-19 vaccines cannot cause infection in anyone. Vaccines are effective at preventing COVID-19 in people who are breastfeeding. Additionally, breastfeeding people who have received mRNA COVID-19 vaccines have antibodies in their breast milk, which could help protect their babies. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine recommend that lactating women receive the vaccine and that breastfeeding should not be stopped around the period of vaccination.
Myth: COVID-19 causes infertility.
Truth: There is no evidence that COVID-19 vaccines cause fertility problems in women or men. The mRNA vaccines are processed by your body near the injection site and activate immune system cells that then travel through the lymph system to nearby lymph nodes. In this manner, they are not affecting hormone levels, nor are they traveling throughout the body or affecting other body organs.
Myth: The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System proves that COVID-19 vaccination causes too many side effects and deaths.
Truth: VAERS data alone cannot determine if an adverse event was caused by a COVID-19 vaccination. Anyone can report individual events to VAERS, even if it is not clear whether a vaccine caused the problem. These events are studied by vaccine safety experts who track for trends, then validate significant adverse concerns. Recently, the number of deaths reported in VAERS has been misinterpreted and misreported as if this number means deaths were proven to be caused by COVID-19 vaccination.
Myth: COMIRNATY vaccine contains fetal cells.
Truth: None of the COVID-19 vaccines contain fetal cells. Specifically, COMIRNATY and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines did not use a fetal cell line to manufacture their vaccine. However, a fetal cell line was used in early research efficacy of these vaccines.
The use of these fetal cell lines in research and/or production of vaccines and medication is not new. Some over-the-counter medications for which a historic fetal cell line was utilized in research and/or production and manufacturing include: Tylenol, Pepto Bismol, Aspirin, Tums, Senokot, Motrin, Maalox, Ex-Lax, Benadryl, Sudafed, Preparation H, Claritin, and others.
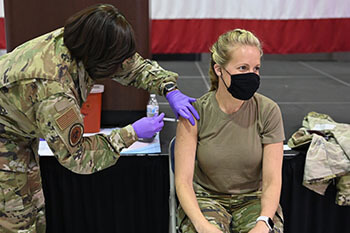 Air Force Master Sgt. Tiffany Sneeze, from the 165th Airlift Wing, administers the COVID-19 vaccination to an Airman in June 2021 on Dobbins Air Force Base, Georgia (Photo by: Army Capt. Amanda Russell, Georgia National Guard).
Air Force Master Sgt. Tiffany Sneeze, from the 165th Airlift Wing, administers the COVID-19 vaccination to an Airman in June 2021 on Dobbins Air Force Base, Georgia (Photo by: Army Capt. Amanda Russell, Georgia National Guard).
Myth: Researchers rushed the development of the COVID-19 vaccine, so its effectiveness and safety cannot be trusted.
Truth: The COVID-19 vaccines in the U.S. have gone through the typical FDA approval process - no steps were skipped - but some steps were conducted on an overlapping schedule to gather data faster.
First, the COVID-19 vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna were created with a method that has been in development for years, so the companies could start the vaccine development process early in the pandemic. Second, vaccine projects received large resources. Governments invested in research and/or paid for vaccines in advance, which enabled a faster approach. Third, some types of COVID-19 vaccines were created using messenger RNA (mRNA), which allows a faster approach than the traditional way that vaccines are made. Fourth, the capabilities of social media reaching numerous people enabled companies to find and engage study volunteers at a faster than typical pace. Finally, COVID-19 is so contagious and widespread, therefore it did not take long to see if the vaccine worked for the study volunteers who were vaccinated.
Myth: If I get the COVID-19 vaccine, it will make me sick with COVID-19.
Truth: You cannot get COVID-19 disease from the COVID-19 vaccine. COVID-19 vaccines teach our immune systems how to recognize and fight the virus that causes COVID-19. Sometimes this process can cause symptoms, such as fever. These symptoms are normal and are signs that the body is building protection against the virus that causes COVID-19. If you do not have side effects, that does not mean your body's immune system is not responding.
Myth: COVID-19 vaccines shed or release their components and are harmful.
Truth: Vaccine shedding is the term used to describe the release or discharge of any of the vaccine components in or outside of the body. Vaccine shedding can only occur when a vaccine contains a weakened live version of the virus. None of the COVID-19 vaccines authorized for use in the U.S. contain a live virus.
Myth: COVID-19 vaccine will alter my DNA.
Truth: COVID-19 vaccines do not change or interact with DNA in any way. Both mRNA and viral vector COVID-19 vaccines deliver instructions (genetic material) to our cells to start building protection against the virus that causes COVID-19. However, the material never enters the nucleus of the cell, which is where our DNA resides.
Myth: Receiving the COVID-19 vaccine will make me magnetic.
Truth: All COVID-19 vaccines are free from metals and will not make anyone magnetic. None of the COVID-19 vaccines contain eggs, gelatin, latex, or preservatives.
Myth: The COVID-19 vaccine contains microchips.
Truth: COVID-19 vaccines do not contain manufactured electronic or microchips. Vaccines are developed to fight against disease and are not administered to track your movement. Vaccines work by stimulating your immune system to produce antibodies. After getting vaccinated, you develop immunity to that disease, without having to get the disease first.
Airmen, Guardians and family members who still have questions and concerns are encouraged to reach out to their primary care provider. Additional information, including the DOD mandate, can be found here.