From Prosthetic Legs to Cranial Implants: How the MHS is using 3D Tech
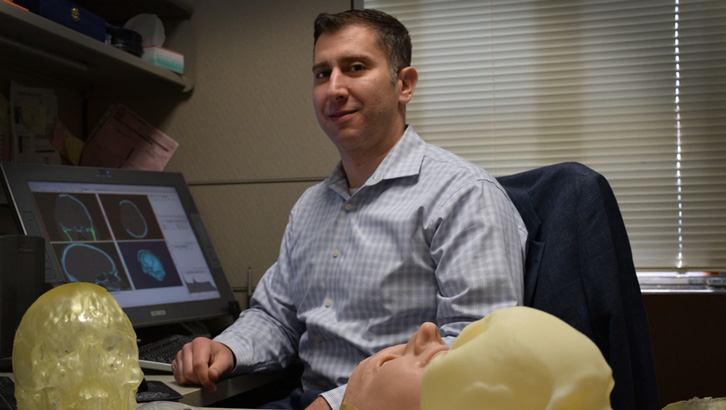 3D MAC Director Peter Liacouras, in a 2017 photo (Photo by: Regina Randolph, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center).
3D MAC Director Peter Liacouras, in a 2017 photo (Photo by: Regina Randolph, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center).
This is the fourth and final in a series of articles on advances in military health care and technology since the Persian Gulf War, 30 years ago this year. See part 1 here, part 2 here, and part 3 here.
Technology for 3D printing is transforming the Military Health System (MHS).
Advances in prosthetics are helping wounded warriors take on activities like ice hockey, rock climbing, and CrossFit. For combat veterans with severe head injuries, sophisticated 3D printing machines can "print" customized cranial implants to restore damaged skulls to their original shape and density. And using 3D tech to make models for doctors to train on is reducing the time required for surgeries and improving outcomes.
These technologies were essentially unheard of 30 years ago in the wake of the first Gulf War. Yet after some initial advances in the 1990s, the MHS began to rapidly increase the use and application of 3D printing after the start of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan.
"During these conflicts, we saw our services expand," said Peter Liacouras, director of services at the 3D Medical Applications Center, known as 3D MAC, which is part of the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland.
Liacouras was the first engineer brought in to Walter Reed Bethesda for 3D applications. "Our primary goal, in the beginning and for the first five or six years, was the 3D printing and 3D reconstruction from medical imaging," he said.
With "stacks" of CT scans or MRI images, they could use 3D printers to construct life-size physical models for providers to hold in their hands. Patient-specific medical models give surgeons the feeling "like they have been there before," improving outcomes, Liacouras said.
 Air Force Staff Sgt. Jonathan Bahr, 312th Training Squadron Special Instruments Training course instructor, and Tech. Sgt. Donald Kramer prepare and don 3D printed face shields at the Louis F Garland Department of Defense Fire Academy on Goodfellow Air Force Base, Texas in March 2020. The instructors got the idea after seeing other organizations modeling and printing these supplies to provide for medical facilities (Photo by: Airman 1st Class Robyn Hunsinger).
Air Force Staff Sgt. Jonathan Bahr, 312th Training Squadron Special Instruments Training course instructor, and Tech. Sgt. Donald Kramer prepare and don 3D printed face shields at the Louis F Garland Department of Defense Fire Academy on Goodfellow Air Force Base, Texas in March 2020. The instructors got the idea after seeing other organizations modeling and printing these supplies to provide for medical facilities (Photo by: Airman 1st Class Robyn Hunsinger).
"One primary application was for the department of neurosurgery, and involved designing custom cranial implants," he explained. "To do this, we would model the skull in the current state, perform mirror imaging techniques, and then adapt the surface by morphing the missing section to the native anatomy. These 'missing sections' were then molded and made into an implantable material."
What started out as a center with two employees and two 3D printers has now evolved into a manufacturing facility with seven employees and more than 10 printers. Materials used for printing include plastic blends, plaster and metal alloys. The 3D-MAC at Walter Reed Bethesda is the largest 3D medical printing facility within the Department of Defense and now incorporates other processes such as 3D scanning, design, and post-production finishing. (See a video overview of the 3D-MAC here.)
3D Printing and Military Medicine
Now, after years of further technological development, 3D printing is being used in the civilian world for everything from toys to architecture to manufacturing. The MHS is using it to enhance beneficiaries' lives by providing pre-surgical models, custom implants, surgical guides, facial prosthetic molds, assistive technology and hand-like devices for amputees.
Specialized prosthetics allow amputees to take part in complex activities such as ice hockey, rock climbing, and cross-fit activities, he said.
Surgical simulators allow providers the ability to practice a procedure before treating an actual patient.
"By printing at the point of care, providers and engineers can work together to solve a particular problem, while reducing cost, time, and the necessity to outsource," he said.
The 3D capability also "aids in [the patients'] mental recovery, by knowing they are no longer limited by their injuries," he added.
 A technician at the 3D MAC center works on dental reconstruction (Photo by: 3D MAC video, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center).
A technician at the 3D MAC center works on dental reconstruction (Photo by: 3D MAC video, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center).
Liacouras said his team went from a lab only producing models of CT/MRI images to now producing dozens of practical items, such as 100 sets of "shorty feet" - devices that help bilateral above-the-knee amputees move like they are walking on their knees. Amputees initially use these devices when they are learning how to walk again, starting them out lower to the ground, and later to walk/lounge around the house, play on the floor with their children, or hang out at the pool. These tasks are sometimes difficult for service members requiring two full-length prosthetics limbs.
Future of 3D
"Our advances in diagnostics in the neuro-imaging space have grown incredibly, including our ability to recreate 3D images of any part of the body," said Dr. Paul Pasquina, a retired Army colonel who is now a professor and chair of the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU) in Bethesda, Maryland.
"It is really amazing," he said.
The printing of 3D organs is still some distance away from reality, Pasquina explained, but the ability to build "basic scaffolds" of certain cells, body tissues, and nerve-grafting has been a major evolution in the technology. And the more sophisticated 3D imaging gets, the more it has helped service members who have lost a limb. Bioprinting efforts are now being performed, researched, and investigated by staff of USU.
In recent years, 3D MAC has added materials like titanium to the mix. They have also collaborated with dentistry and other departments throughout the hospital to print devices like maxillofacial prosthetic molds, Liacouras said.
Elsewhere, 3D printing is one of four lines of effort meant to push forward the curriculum and instructional delivery at the Medical Education and Training Campus at Joint Base San Antonio-Fort Sam Houston, Texas. The 3D printed simulation models allow students and other trainees to gain exposure to a variety of technological tools and procedures.
Despite these exciting medical advances involving 3D imaging and 3D printing, significant scientific and regulatory challenges remain. Liacouras and Pasquina agree more transformative applications for this technology will need time to evolve.