The cancer risk for the active component military population may differ from the general U.S. population due to differences in behavioral exposures such as alcohol and tobacco use1 as well as deployment or occupational-related exposures.2-4 This Surveillance Snapshot presents the incidence of the 10 leading cancers among active component service members diagnosed from January 2018 through December 2022. Cancer cases were defined using Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division case definitions, which are based on administrative diagnostic codes under the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10).5 For cancers without an existing AFHSD case definition, the following criteria classified a case: an inpatient encounter with a qualifying ICD-10 diagnostic code in the first diagnostic position (dx1); or an inpatient encounter with a qualifying diagnostic code in the second diagnostic position (dx2) and a treatment code (ICD-9: V580, V581*; ICD-10: Z510*, Z511*) in dx1; or 3 or more outpatient encounters within a 90-day period (but not on the same day) with a qualifying diagnostic code in dx1 or dx2. A cancer was counted once per person in a lifetime based on earliest diagnosis. Rates were calculated per 100,000 person-years, accounting for sex-specific rate calculations to female breast, testis, and prostate cancers.
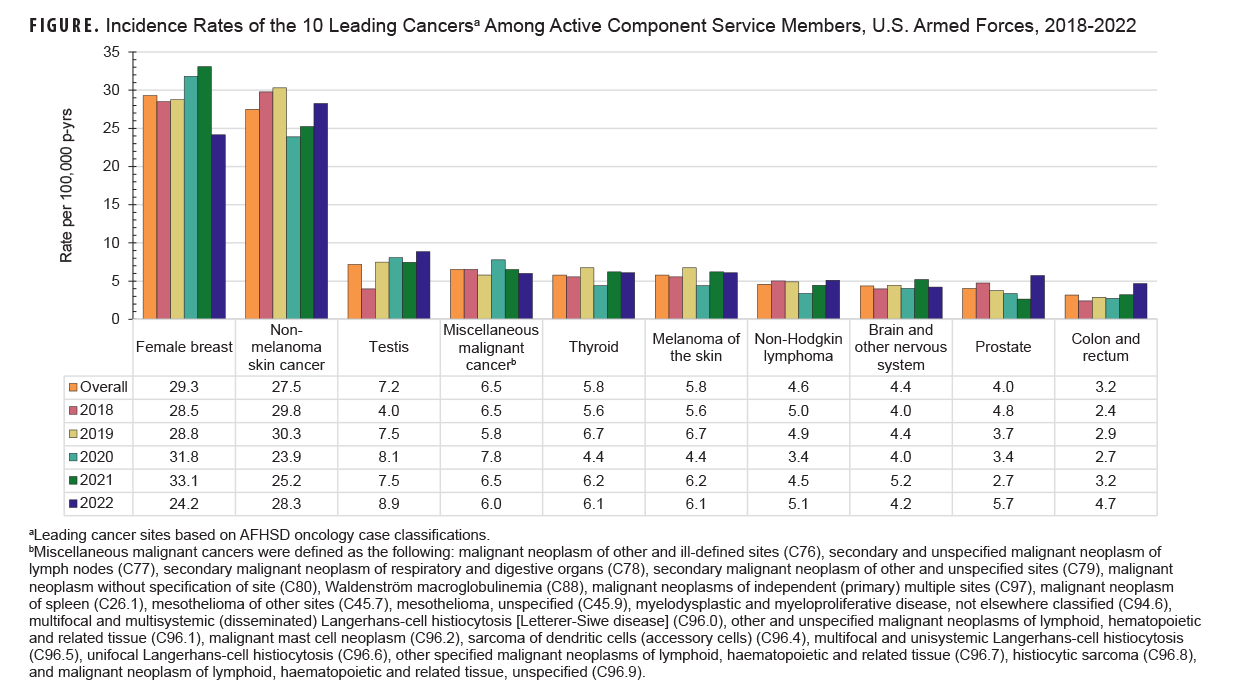
Cases were classified for all ICD-10 Chapter 2 malignant neoplasms (C00-C96) to identify the leading cancer sites. Overall, there were 6,635 total incident cancer cases from 2018 to 2022; 77.5% (n=5,146) of these cases represented the leading 10 cancers among ACSM. Non-melanoma skin cancer (n=1,851) was the most frequent cancer, followed by testicular cancer (n=602), miscellaneous malignant cancer (n=484), thyroid cancer (n=440), and melanoma of the skin (n=391). The annual fluctuations in the incidence rate of diagnoses for each cancer are shown in the Figure. Overall, female breast cancer had the highest incidence over the 5-year surveillance period.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy of the Department of Defense nor the U.S. Government.
Author Affiliations
Defense Health Agency, Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division, Epidemiology and Analysis (Dr. Mabila, Ms. Dreyer).
References
- Weese CB, Abraham JH. Potential health implications associated with particulate matter exposure in deployed settings in southwest Asia. Inhal Toxicol. 2009;21(4):291-296. doi: 10.1080/08958370802672891
- Aurell J, Gullett BK, Yamamoto D. Emissions from open burning of simulated military waste from forward operating bases. Environ Sci Technol. 2012;46(20):11004-11012. doi: 10.1021/es303131k
- Lowers HA, Todorov R, Strand MJ, et al. Lung biopsies from symptomatic military deployers have variable mineral particle types and higher abundances of silicon, aluminum, cadmium and vanadium compared to controls. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191:A2575. doi: 10.3322/caac.21601
- Meadows SO, Engel CE, Collins RE, et al. 2018 Department of Defense Health Related Behaviors Survey (HRBS): Results for the Active Component. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2021. Accessed August 25, 2023. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RR4222.html
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division. Surveillance Case Definitions. Accessed September 1, 2023. https://www.health.mil/Military-Health-Topics/Health-Readiness/AFHSD/Epidemiology-and-Analysis/Surveillance-Case-Definitions