Chikungunya is a viral disease spread by the bite of an infected mosquito,1 characterized by severe joint pain and myalgia that can last for weeks or months.2 Prior to 2013, cases and outbreaks of Chikungunya were identified in Africa, Asia, and Europe; in late 2013, however, the first local transmission in the Americas was identified in the Caribbean.1 Chikungunya became a nationally-notifiable disease in the United States in 2015 following a substantial increase in locally-acquired infections reported in U.S. territories.3
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced its approval of a live attenuated virus vaccine on November 9, 2023, which may eventually be recommended to U.S. travelers.4 This could become relevant for U.S. military service members at potential risk for Chikungunya virus infection during deployments to endemic locations, particularly during outbreaks among local populations.
Prior MSMR reports describe cases of Chikungunya occurring among U.S. military service members and other beneficiaries between 2010 and 2020.5,6 This Surveillance Snapshot updates these results through the end of 2022, using confirmed and probable medical event reports of Chikungunya cases from the U.S. military’s Disease Reporting System internet, which were confirmed via medical chart review.
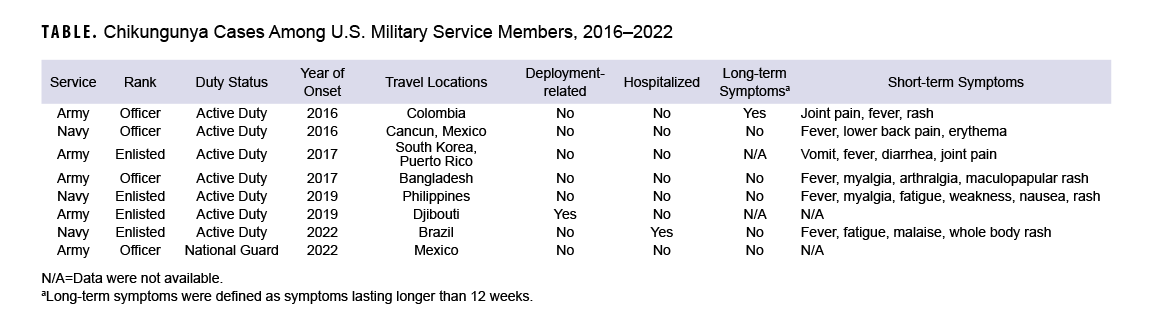
Eight cases of Chikungunya virus disease among service members were documented between 2016 and 2022 (Table). Five cases were recorded in the Army, and three in the Navy. One case was acquired while on deployment to Djibouti; no other cases were deployment-related. Two cases were acquired via unofficial travel to Mexico. One case each was attributed to unofficial travel to Colombia, Brazil, Bangladesh, and the Philippines. Another case was diagnosed during deployment to South Korea, but the DRSi record indicated that the patient had previously lived in Puerto Rico, with no other pertinent travel history.
Only one case was hospitalized; this case was acquired in Brazil by a 35-year-old male with a medical history of Bell’s palsy. Five cases reported fever and myalgia, which were the most commonly documented symptoms. Other reported symptoms included nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and rash. One case involving a 30-year-old male who acquired the infection in Colombia evidenced long-term symptoms (i.e., lasting longer than 12 weeks) manifesting as bilateral wrist and ankle pain worsened by movement.
The small number of cases, hospitalizations, and evidence of long-term symptoms reported in the past seven years suggest that risk of Chikungunya virus disease to U.S. service member readiness is small. Prior reports have, however, indicated that cases among U.S. service members increase during periods of outbreak among local populations.6 Therefore, service members deployed to endemic locations are encouraged to use standard preventive measures including use of personal protective equipment. Policy development may also benefit from this information as the FDA-approved vaccine becomes more widely available.
Authors' Affiliation
Defense Health Agency, Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division, Epidemiology and Analysis Section
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chikungunya Virus. Accessed Nov. 1, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/chikungunya/index.html
- de Lima Cavalcanti TYV, Pereira MR, de Paula SO, Franca RFO. A review on Chikungunya virus epidemiology, pathogenesis and current vaccine development. Viruses. 2022;14(5):969. doi:10.3390/v14050969
- Mourad O, Makhani L, Chen LH. Chikungunya: an emerging public health concern. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2022;24(12):217-228. doi:10.1007/s11908-022-00789-y
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA News Release: FDA Approves First Vaccine to Prevent Disease Caused by Chikungunya Virus. Nov. 9, 2023. Accessed Dec. 8, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-vaccine-prevent-disease-caused-chikungunya-virus
- O'Donnell FL, Fan M, Stahlman S. Surveillance for vector-borne diseases among active and reserve component service members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2016-2020. MSMR. 2021;28(2):11-15.
- O'Donnell FL, Stahlman S, Fan M. Surveillance for vector-borne diseases among active and reserve component service members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2010-2016. MSMR. 2018;25(2):8-15.