 This Surveillance Snapshot provides the first summary of the demographic composition of active component Space Force service members, as of November 2023. This Snapshot is intended to inform future MSMR illness and injury surveillance reports about this population.
This Surveillance Snapshot provides the first summary of the demographic composition of active component Space Force service members, as of November 2023. This Snapshot is intended to inform future MSMR illness and injury surveillance reports about this population.
The U.S. Space Force was established in December 2019 to secure the United States’ interests in, from, and to outer space.1 The Space Force is a separate and distinct branch of the armed services, although it is organized under the Department of the Air Force. The Space Force provides space capabilities to the joint forces by managing space launch operations and maintaining a global satellite surveillance network that provides in-theater secure communications, as well as weather and navigation information, for military operations, in addition to threat warning.
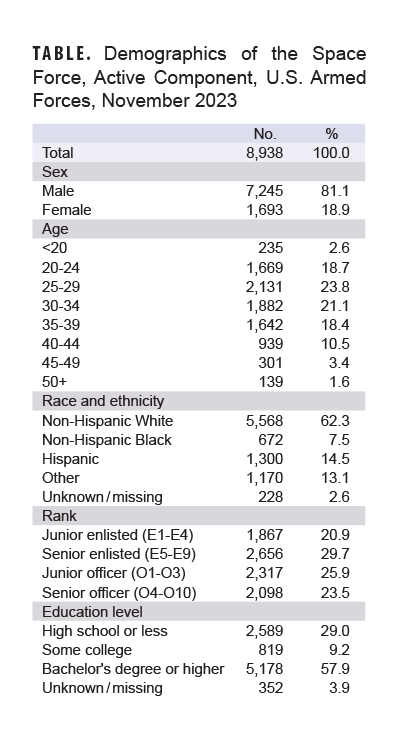
The Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division began receiving personnel and demographic information about Space Force members from the Defense Manpower Data Center in 2023. As of November 2023, there were 8,938 active component members of the U.S. Space Force (Table). The majority were male (81.1%), non-Hispanic White (62.3%), and possessed a bachelor’s degree or higher (57.9%). The largest proportion of service members within 5-year age categories were classified as 25-29 years (23.8%) and 30-34 years (21.1%). There was a roughly even proportion of junior officers (25.9%) and senior officers (23.5%), while there were more senior enlisted (29.7%) than junior enlisted (20.9%) members.
The Space Force bases with the highest percentages of active component Space Force members assigned were Schriever SFB, CO (18.7%), Peterson SFB, CO (15.6%), Vandenberg SFB, CA (9.4%), Buckley SFB, CO (8.4%), and Los Angeles SFB, CA (7.4%). Roughly half of the 8,938 Space Force members were missing an occupation code as of November 2023. Of those with a valid occupation code, the most common occupations were Operations Staff Officers (42.3%) and Procurement and Production Officers (18.2%) (data not shown).
Active component Space Force members are demographically similar to other active component service members: The majority are males and non-Hispanic White.2 The data presented in this report suggest, however, that Space Force members are, on average, older and more highly educated than the overall active component.2 In 2022, 34.2% of all ACSM were aged 24 years or younger and 34.9% held a bachelor’s degree or higher, compared to 21.3% of Space Force members aged 24 years or younger and 57.9% with a bachelor’s degree or higher. These findings may be used to help interpret future MSMR illness and injury surveillance reports on the Space Force.
References
- United States Space Force. About the Space Force. Accessed Jan. 19, 2024. https://www.spaceforce.mil/About-Us/About-Space-Force
- McQuistan AA, Dreyer E, Mabila SL. Surveillance snapshot: mid-year populations by sex, age, and race and ethnicity of active component service members of the U.S. Armed Forces, 2018–2022. MSMR. 2023;30(12):12. https://www.health.mil/News/Articles/2023/12/01/MSMR-MidYear-Populations