Blood donations remain vital for Service Member care
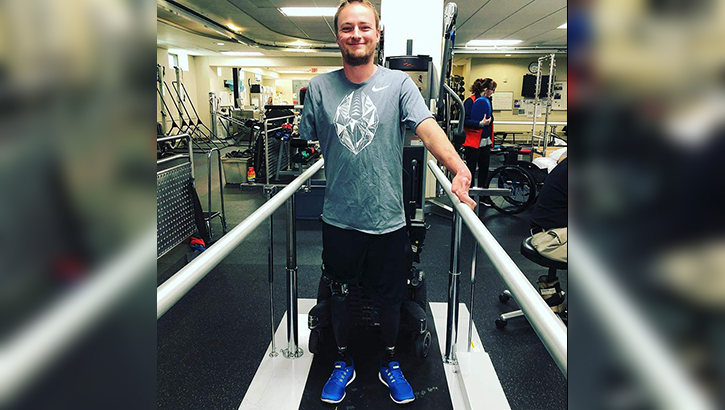 Jason Hallett underwent physical therapy at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland after recovering from osseointegration, a complicated procedure where a prosthetic limb is surgically anchored and integrated into the patient’s bone. (Courtesy photo.)
Jason Hallett underwent physical therapy at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland after recovering from osseointegration, a complicated procedure where a prosthetic limb is surgically anchored and integrated into the patient’s bone. (Courtesy photo.)
The Armed Services Blood Program is the military's only blood donor program for service members, their families, retirees, veterans, and local communities worldwide, helping those in critical need. Both whole blood and COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma from those who have recovered from COVID-19 remain in high demand. All 21 donor centers adhere to CDC guidelines to reduce the spread of COVID-19.
When it comes to the need for donated blood, soldiers on the battlefield understand. For Marines witnessing a member of their unit in danger of losing life or limb, it locks in quickly. They instinctively begin lining up to give because they see the human face behind the small needle sting and the hanging bag of blood.
Those in charge of military blood banks want stateside donors to see this face, too. Look no further than former Marine Cpl. Jason Hallett, who as a minesweeper serving in Afghanistan in 2010 lost both his legs above the knee, his right arm over the elbow, and fingers from his left hand, among other wounds.
Blood donation “is definitely one of those things that when you’re actually needing it, it’s front-of-mind,” Hallett said from his home in Windsor, Colorado. “To get people motivated who do not see a right-away need for it, it’s just a matter of getting into a right mindset.”
Air Force Lt. Col. Valerie Sams, trauma medical director at Brooke Army Medical Center at Joint Base San Antonio in Texas agrees.
“For military members, it’s really easy downrange to see it, but it’s kind of ‘out of sight, out of mind’ sometimes,” Sams said. “I think people don’t realize operations are still ongoing, even today. And we have brothers and sisters out there in harm’s way that are getting injured. So, when you’re back home in your local military treatment facility, it probably doesn’t reach that level of criticality, but downrange, it does.”
While there’s a need for all blood types, the universal donor, O-negative, is always in particularly high demand.
 Air Force Lt. Col. (Dr.) Valerie Sams, right, serving as trauma czar and operating on a combat casualty at Craig Joint Theater Hospital, Bagram Airfield, Afghanistan, in 2019. (Courtesy Photo.)
Air Force Lt. Col. (Dr.) Valerie Sams, right, serving as trauma czar and operating on a combat casualty at Craig Joint Theater Hospital, Bagram Airfield, Afghanistan, in 2019. (Courtesy Photo.)
Hallett explained that he has no idea of how much donated blood has coursed through his system over the years, but it’s fair to say quite a bit. He was in three major military hospitals over four months after his trauma, and lost count of the number of surgeries and blood transfusions he underwent. Some of them were lost in memory due to medically induced comas. As if that weren’t enough, his body often had bad reactions to the blood he received, such as iron deficiency or extreme fatigue, meaning that yet another transfusion was needed to stabilize him.
“Any surgery that I had, there had to be a follow-up transfusion,” he recalled.
Hallett has not needed blood in well over a year, since he underwent “osseointegration,” a complicated procedure when a limb prosthesis is permanently, surgically anchored and integrated into the patient’s own bones and flesh. He spoke of this all matter-of-factly, so when he talks of re-framing the issue of blood donation, his experience shows.
“For people stateside, I guarantee that there are people they know who have had to have a transfusion,” he said. “It’s just getting that story, and that background — that ‘if this person that I’m close to didn’t have a transfusion, they’d probably not be here right now, or they would have some significant issues.’”
Hallett likened the blood supply to car insurance.
“If you don’t have it and all of a sudden you need it, it’s like, ‘Oh, crap,’” he said.
 Former Marine Cpl. Jason Hallett cuddles with his twins, Jason Jr., and Marina. Hallett was severely injured when he stepped on an improvised explosive device in Sangin, Afghanistan on Oct. 23, 2010 Thanks in part to lifesaving measures, multiple surgeries and dozens of blood transfusions, he was able to become a father to the twins in October 2016. (Courtesy Photo)
Former Marine Cpl. Jason Hallett cuddles with his twins, Jason Jr., and Marina. Hallett was severely injured when he stepped on an improvised explosive device in Sangin, Afghanistan on Oct. 23, 2010 Thanks in part to lifesaving measures, multiple surgeries and dozens of blood transfusions, he was able to become a father to the twins in October 2016. (Courtesy Photo)
Hallett said he’s amenable to helping with getting the message out about the critical need for blood donors, speaking from example. More blood drives that partner with wounded warrior organizations could help that.
“I don’t think a lot of people are very open with stuff like that,” he said. “I do think having people like me that are wanting to share that, it’s kind of important. I think it would be very, very helpful.”
Others in the military who have served overseas and who previously could not give blood might now be eligible, due to sweeping changes implemented by the ASBP last summer that will allow thousands more to donate. The changes were in response to updates in guidance from the Food and Drug Administration.
When asked if it was safe to say that if more people gave blood, it would directly save more lives on the battlefield, Sams did not hesitate.
“Absolutely,” she said, adding that service members have died because of battle injuries followed by not enough blood on hand, or not enough available in the so-called “golden hour” after a grievous injury.
“In the forward environment at the point of injury, that has happened, and we know that’s the number one cause of mortality in combat — those patients that were injured who needed both blood and surgical control of their bleeding, and they couldn’t get it in time.”
Blood drives and walking blood banks in forward areas are very successful, Sams said. But as Hallett alluded to, when the urgency is not present, often the donors aren’t, either.
“When there are multiple injured soldiers, their units show up, and line up by the tens to hundreds to donate,” she said. “It’s a little bit trickier in garrison when people are just going about their normal lives. It’s just not at the forefront of their mind. As we advertise these blood drives, we need to tie it back to that.”
That means tying it to the trauma suffered by civilians on the home front, too. Giving blood so it can be delivered only to the front lines overseas is not really the point, Sams said. “But when we’re doing these blood drives, it needs to be tied to the reason we do everything we do, and that’s to save lives on the battlefield. That’s the whole purpose of our existence.”
Donated blood also benefits wounded warriors who are stateside, as many of them are in need of multiple surgeries over the course of months, or even years. And yet, even a proselytizer like Hallett realizes that the importance of blood donations can be easily forgotten. He was confronted with that understanding when, more than four years ago, his ex-wife gave birth to twins. Because she had to have a C-section, she needed a transfusion. After all the blood he had received over the years, it gave him pause.
“We have to remind folks. Most people who donate, donate multiple times,” Sams said. “They donate every chance they get. Once folks make the connection, they will become a sustaining donor, but we have to help them make that connection sometimes. I think we should do a little better job of that when we’re doing the blood drives.”
Sams backs up her words with action, and says the kind of medicine she practices has influenced her desire to donate her own blood frequently. And a good thing, too. Her blood type is O-negative.