Donovanosis, or granuloma inguinale, is an uncommon sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is much rarer than chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Donovanosis is found mainly in tropical regions, and is highly correlated with populations affected by poverty and lack of access to hygiene and public health infrastructure. However, recent news reports have described donovanosis as a "flesh-eating" STI that may be increasing in incidence in developed countries.1–3
Donovanosis is a bacterial infection of the skin and mucous membranes in the genital region.4–5 Early lesions are small, painless nodules that grow into characteristic "beefy red" highly vascular ulcers and progressively expand. Untreated cases can result in tissue destruction and scarring. Although clinical diagnosis is possible, ulcers may be hard to differentiate from those associated with syphilis, chancroid, HIV-associated herpes, amoebiasis, and carcinoma. For this reason, confirmation via staining of tissue or biopsies is recommended. The causative agent is Klebsiella granulomatis, a gram-negative intracellular bacillus, which produces characteristic Donovan bodies within mononuclear cells upon staining. Antibiotics such as azithromycin, doxycycline, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are curative over a 3-week course or until sores have healed.
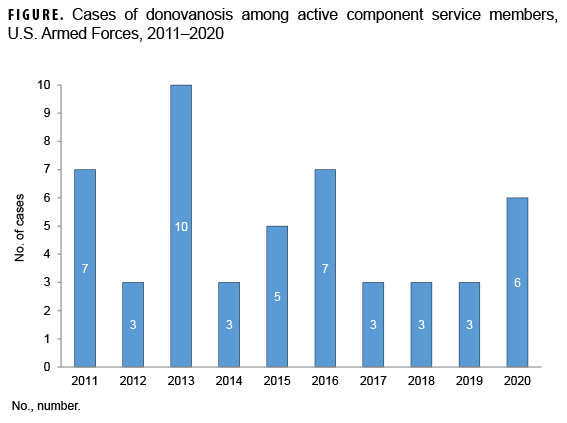
For this analysis, the Defense Medical Surveillance System was searched for records of inpatient and outpatient care for diagnoses of donovanosis. A case was defined by the recording of 1 inpatient or outpatient diagnosis of donovanosis (International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision Clinical Modification [ICD-9-CM]: 099.2; ICD-10-CM: A58) in the primary diagnostic position. An individual could be counted as an incident case only once during the surveillance period (2011–2020). The surveillance population included all individuals who served in the active component of the Army, Navy, Air Force, or Marine Corps at any time during this period. During the 10-year period, there were 50 incident cases of donovanosis. Cases were split relatively evenly by sex (female service members: 54%; male service members: 46%) and most cases occurred in those aged 20–29 (56%) (data not shown). The annual numbers of cases ranged from 3 to 10 with no discernable trend over time (Figure).
Although the incidence of donovanosis has been very low among service members, it is important for health care providers to be aware of trends of emerging STIs particularly among young, sexually active individuals who may travel to endemic areas. As with other STIs, the best prevention of donovanosis is protected sex.
Author Affiliations: Defense Health Agency, Armed Force Health Surveillance Division (Ms. Daniele and Mr. Wilkerson).
References
- Purves R. Doctors warning as 'flesh-eating' STI hits UK. Birmingham Live. 21 Oct. 2021. Accessed 22 Nov. 2021. https://www.birminghammail.co.uk/news/health/what-donovanosis-flesh-eating-sti-21924441
- Lee B. Donovanosis: Why this is called a 'flesh eating' sexually transmitted infection. Forbes. 24 Oct. 2021. Accessed 22 No. 2021. https://www.forbes.com/sites/brucelee/2021/10/24/donovanosis-why-this-is-called-a-flesh-eating-sexually-transmitted-infection/?sh=423fc60112b4
- Gardiner, Alistair. Should doctors be concerned over this 'flesh-eating' STD? MDLinx. 4 Nov. 2021. Accessed 22 Nov,r 2021. https://www.mdlinx.com/article/should-doctors-be-concerned-over-this-flesh-eating-std/yKQ59ow980YmcCNPqVxiR
- Satter EK. Granuloma inguinale (donovanosis). Mescape. Updated 25 Oct. 2021. Accessed 22 Nov. 2021. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1052617
- O'Farrell N. Donovanosis. Sex Transm Infect. 2002;78(6):452–457.