Sepsis is a serious and life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection.1 In the U.S., sepsis is a leading cause of in-hospital mortality2 and one of the most expensive conditions treated in U.S. hospitals.3
A 2018 retrospective analysis of more than 2 million U.S. sepsis hospitalizations reported that the median length of stay (LOS) for sepsis increased with disease severity ranging from 7.7 days, 10 days, and 12.6 days for sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock, respectively.4
A recent MSMR analysis by Snitchler et al. summarized sepsis hospitalizations diagnosed in active component military members between 2011 and 2020.5 During the 10-year surveillance period, crude overall incidence was 39.8 hospitalizations per 100,000 person-years. Annual incidence rates of sepsis hospitalizations increased 64% from 2011 through 2019, then dropped considerably in 2020.5
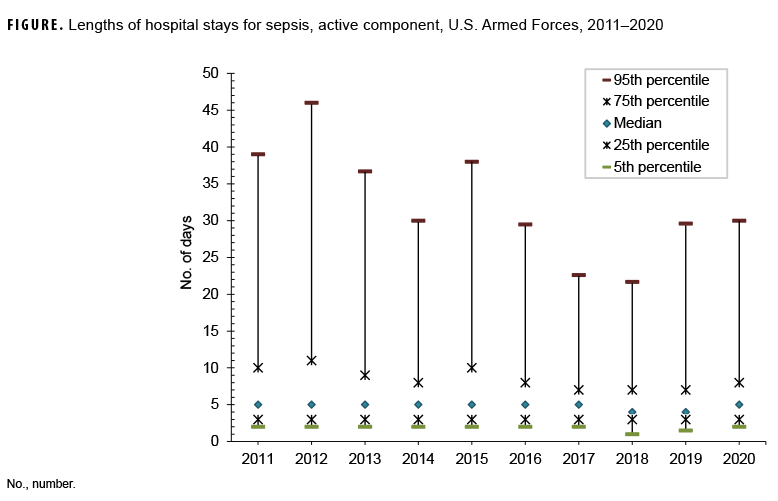
This snapshot summarizes median LOS metrics for sepsis hospitalizations by year during the same surveillance period (Figure). The median LOS for sepsis was 5 days for the period from 2011 through 2017 and declined to 4 days for the years 2018 and 2019. In 2020, the median LOS increased back to 5 days.
Disclaimer: The content of this manuscript is the sole responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, or policies of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, the Department of the Navy, the Department of Defense, or the United States Government. Mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations does not imply endorsement by the United States Government.
References
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801–810.
- Liu V, Escobar GJ, Greene JD. Hospital deaths in patients with sepsis from 2 independent cohorts. JAMA. 2014;312:90–92
- Torio CM, Moore BJ. National inpatient hospital costs: the most expensive conditions by payer, 2013. May, 2016. Accessed 1 Nov 2021. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb204-Most-Expensive-Hospital-Conditions.pdf
- Paoli CJ, Reynolds MA, Sinha M, Gitlin M, Crouser E. Epidemiology and costs of sepsis in the United States-An analysis based on timing of diagnosis and severity level. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(12):1889–1897.
- Snitchler CL, Patel DM, Stahlman SL, Chauhan AV, Wells NY, McQuistan, AA. Sepsis hospitalizations among active component service members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2011–2020. MSMR. 2021;28(11):2–8.