Zika virus is an arboviral infection transmitted primarily through Aedes mosquitoes in tropical and subtropical regions. Although most infections are asymptomatic or mild, Zika virus infection during pregnancy can lead to infant complications and congenital abnormalities.1 In the U.S., the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported 5,559 travel-associated and 231 locally-acquired Zika virus cases from 2015 to 2021.2 The majority of these cases (n=5,168) were identified in 2016, which translates to a peak of 1.6 confirmed or probable noncongenital Zika virus cases per 100,000 persons in the U.S.3,4
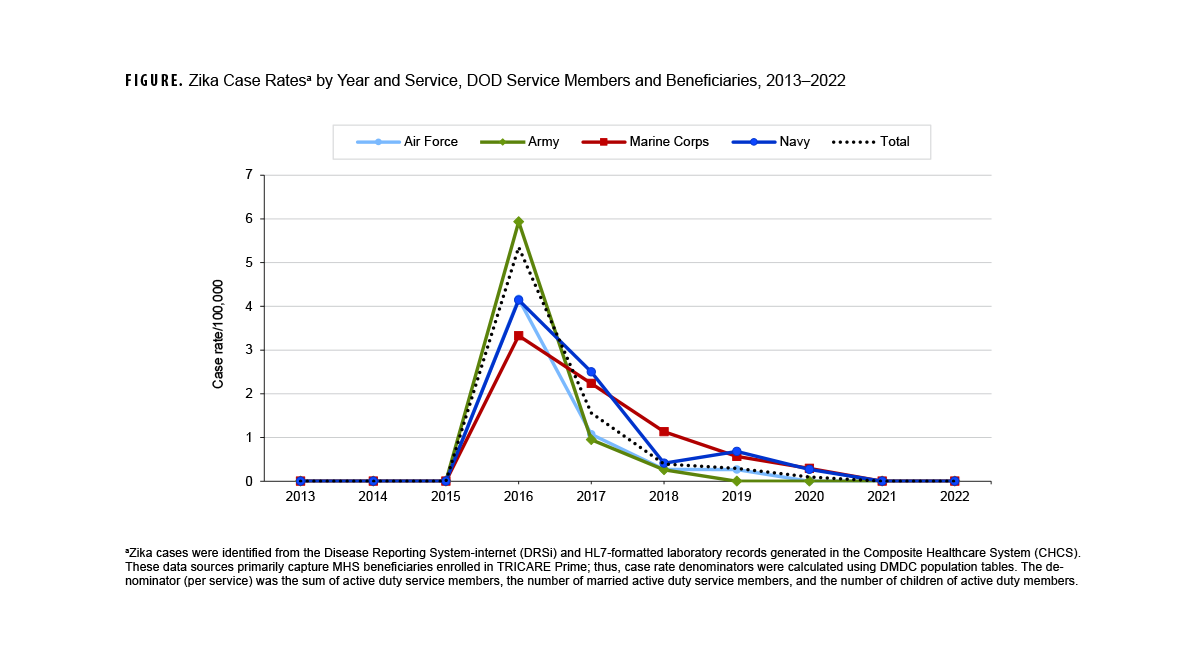
From January 1, 2013 through December 31, 2022, 212 Zika virus cases were detected among Department of Defense service members and beneficiaries. Zika virus’s presentation in the Western Hemisphere in early 20155 led to peak rates (n=143) for all services in 2016, which declined substantially thereafter, until no cases were identified among DOD beneficiaries from 2021 to 2022.
Zika virus cases described in this Snapshot reflect documentation from the Disease Reporting System-internet and laboratory records generated from the Composite Healthcare System. The DRSi Zika virus reporting option was not available until July 2017,6 and until then a medical event report from DRSi included those entered as “Any other unusual condition not listed” that contained case report notes indicating a positive Zika case. Cases indicated by laboratory records include culture identification, antigen detection, nucleic acid detection, and plaque reduction neutralization test detection. Immunoglobulin M-positive cases were included in the absence of PRNT testing.
The rates depicted in this figure were estimated from the number of service members and dependents most likely enrolled in TRICARE Prime, as DRSi reports and CHCS laboratory records primarily reflect individuals with Click to closeDirect CareDirect care refers to military hospitals and clinics, also known as “military treatment facilities” and “MTFs.”direct care at a military clinic or hospital. These population estimates do not clearly delineate risk for services more likely to deploy, travel, or live in assigned unit areas with endemic risk.
Author Affiliations
Defense Centers for Public Health—Portsmouth (Mr. Seliga, Ms. Touchstone, Mr. Matsumoto); Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine, Inc. (Mr. Matsumoto)
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, the U.S. Government, nor the Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine. Kati Touchstone, Kenji Matsumoto, and Nicholas Seliga are employees of the U.S. Government. This work was prepared as part of their official duties. Title 17, U.S.C., §105 provides that copyright protection under this title is not available for any work of the U.S. Government. Title 17, U.S.C., §101 defines a U.S. Government work as a work prepared by a military Service member or employee of the U.S. Government as part of that person’s official duties. This material is based upon work supported by the DOD Information Analysis Center Program Management Office, sponsored by the Defense Technical Information Center under Contract FA807518D0011.
References
- World Health Organization. Zika virus. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/zika-virus
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Zika cases in the United States. Published January 13, 2023. Accessed February 14, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/zika/reporting/index.html
- Hall V, Walker WL, Lindsey NP, et al. Update: noncongenital zika virus disease cases–50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia, 2016. MMWR. 2018;67(9):265-269.
- United States Census Bureau. American Community Survey 5-Year Estimate Data Tables, 2016. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://data.census.gov/table?tid=ACSDP5Y2016.DP05
- Poss DE, Writer JV, Harris S. Zika virus infections in Military Health System beneficiaries since the introduction of the virus in the Western Hemisphere, 1 January 2016 through 30 November 2016. MSMR. 2016;23(12):7-11.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division. Zika virus. Updated December 2017. Accessed March 13, 2023. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2017/12/01/Zika-Virus