This Surveillance Snapshot describes the mid-year population for active component service members of the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard between 2018 and 2022, stratified by age, sex, and race and ethnicity. Population counts were obtained from June of each calendar year using personnel data from the Defense Manpower Data Center maintained within the Defense Medical Surveillance System. Counts and percentages were stratified by sex, age group, and race and ethnicity. Both sex and race/ethnicity are self-reported by the service member. Race and ethnicity were categorized into non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and Other/unknown. As some services do not provide separate race and ethnicity categories for Asian/Pacific Islanders and American Indian/Alaskan Natives, these groups are included in the Other/unknown category.
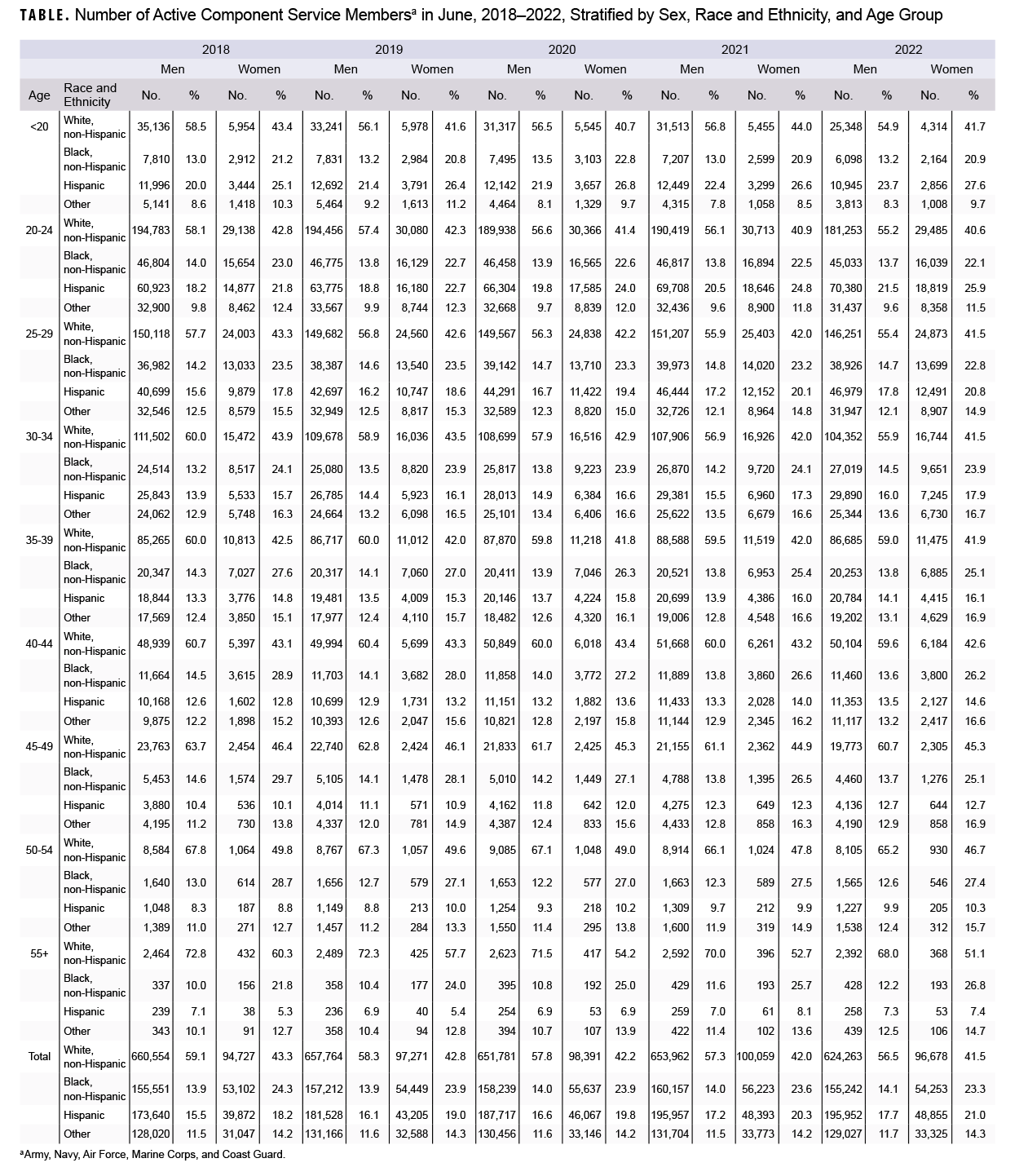
Among ACSM, the minimum and maximum mid-year populations ranged from 1,104,484 to 1,141,780 men and 218,748 to 238,448 women during the surveillance period, with the highest population documented in 2021 for both men and women. The overall proportion of women and Hispanic service members increased between 2018 and 2022, while the proportion of non-Hispanic Whites and service members under 20 years of age decreased. When stratified by sex, age, and race and ethnicity, the racial/ethnic differences between ACSM men and women are apparent (Table). In 2022, non-Hispanic White males represented 56.5% of male ACSM, whereas less than half (41.5%) of female ACSM identified as non-Hispanic White. The proportion of non-Hispanic White male and female ACSM decreased throughout the surveillance period. Among men, the proportion of Hispanics increased throughout the surveillance period; however, they represented a smaller proportion of the older age groups, particularly over 50 years of age. Among women, the proportion of Hispanic service members also increased throughout the surveillance period, and they were typically younger.
Authors' Affiliation
Defense Health Agency, Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division, Epidemiology and Analysis Section